Clofarabine Enhances the Transduction Efficiency of Recombinant AAV2 in the Retina
- PMID: 40434346
- PMCID: PMC12126128
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.66.5.42
Clofarabine Enhances the Transduction Efficiency of Recombinant AAV2 in the Retina
Abstract
Purpose: Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors, a class of antineoplastic agents, were investigated for their ability to enhance recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 2 (rAAV2) transduction in the mouse retina and their underlying mechanisms.
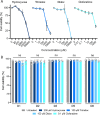
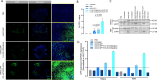
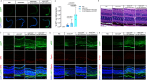
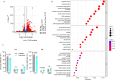
Methods: Candidate ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors were screened in ARPE-19 cells to identify concentrations preserving cell viability while optimizing rAAV2 transduction. Clofarabine, which demonstrated superior enhancement of rAAV2 in vitro, was selected for in vivo evaluation via subretinal coadministration with rAAV2.GFP in mice. Transcriptomic mechanisms were dissected using RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) of clofarabine-treated ARPE-19 cells and single-cell RNA-seq of murine retinas after combinatorial treatment.
Results: Cellular viability assays demonstrated that clofarabine pretreatment significantly enhanced rAAV2.GFP transgene expression in ARPE-19 cells, elevating both mRNA and protein levels compared with rAAV2.GFP transduction alone. This enhancement was mirrored in vivo, where subretinal coadministration of clofarabine with rAAV2.GFP in mice increased retinal transduction efficiency markedly, without detectable toxicity. Transcriptomic profiling delineated clofarabine's mechanism. (1) In proliferating cells, it triggered S-phase arrest by upregulating CCNE2 and CDC6, synchronizing cell populations to optimize viral genome processing; and (2) in postmitotic retinal cells, it suppressed innate immune pathways while enhancing nucleotide biosynthesis and transcriptional activity, thereby creating a microenvironment permissive to rAAV transduction.
Conclusions: Clofarabine safely enhances rAAV2 transduction efficiency in both ocular cell models and murine retinas. Its ability to synchronize cell cycles in dividing cells and reprogram transcriptional landscapes in postmitotic cells positions it as a promising adjunct for rAAV-based ocular gene therapy, potentially decreasing therapeutic vector doses and improving clinical outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enhancement of rAAV2-mediated transgene expression in retina cells in vitro and in vivo by coadministration of low-dose chemotherapeutic drugs.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 May 4;53(6):2675-84. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8856. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22427581
-
Improvement of Photoreceptor Targeting via Intravitreal Delivery in Mouse and Human Retina Using Combinatory rAAV2 Capsid Mutant Vectors.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Dec 1;58(14):6429-6439. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-22281. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 29260200 Free PMC article.
-
The use of melittin to enhance transgene expression mediated by recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 2 vectors both in vitro and in vivo.J Integr Med. 2023 Jan;21(1):106-115. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2022.10.003. Epub 2022 Oct 10. J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 36333178
-
Melittin analog p5RHH enhances recombinant adeno-associated virus transduction efficiency.J Integr Med. 2024 Jan;22(1):72-82. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2024.01.001. Epub 2024 Jan 17. J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 38307819
-
Transduction of pancreatic islets with pseudotyped adeno-associated virus: effect of viral capsid and genome conversion.Transplantation. 2005 Sep 15;80(5):683-90. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000173381.97556.0d. Transplantation. 2005. PMID: 16177645
References
-
- Kaplitt MG, Feigin A, Tang C, et al. .. Safety and tolerability of gene therapy with an adeno-associated virus (AAV) borne GAD gene for Parkinson's disease: an open label, phase I trial. Lancet (London, England). 2007; 369: 2097–2105. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

