The antiangiogenic peptide VIAN-c4551 inhibits lung melanoma metastasis in mice by reducing pulmonary vascular permeability
- PMID: 40435350
- PMCID: PMC12118997
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316983
The antiangiogenic peptide VIAN-c4551 inhibits lung melanoma metastasis in mice by reducing pulmonary vascular permeability
Abstract
Introduction: Cancer cells drive the increase in vascular permeability mediating tumor cell extravasation and metastatic seeding. VIAN-c4551, an antiangiogenic peptide analog of vasoinhibin, inhibits the growth and vascularization of melanoma tumors in mice. Because VIAN-c4551 is a potent inhibitor of vascular permeability, we evaluated whether its antitumor action extended to a reduction in metastasis generation.
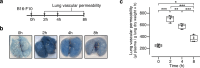
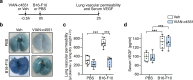
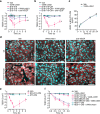
Methods: Circulating levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), lung vascular permeability, melanoma cell extravasation, and melanoma pulmonary nodules were assessed in C57BL/6J mice intravenously inoculated with murine melanoma B16-F10 cells after acute treatment with VIAN-c4551. VEGF levels, transendothelial electrical resistance, and transendothelial migration in cocultures of B16-F10 cells and endothelial cell monolayers supported the findings.
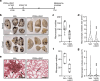
Results: B16-F10 cells increased circulating VEGF levels and elevated lung vascular permeability 2 hours after inoculation. VIAN-c4551 prevented enhanced vascular permeability and reduced melanoma cell extravasation after 2 hours and the number and size of macroscopic and microscopic melanoma tumors in lungs after 17 days. In vitro, VIAN-c4551 suppressed the B16-F10 cell-induced and VEGF mediated increase in endothelial cell monolayer permeability and the transendothelial migration of B16-F10 cells. No detrimental effect of VIAN-c4551 was observed on hematological, biochemical, and histological parameters after its intravenous administration in mice for 14 days.
Conclusions: These findings support the inhibition of distant vascular permeability for the prevention of tumor metastasis and unveil the anti-vascular permeability factor VIAN-c4551 as a potential and safe therapeutic drug able to prevent metastasis generation by lowering the extravasation of melanoma cells.
Copyright: © 2025 Perez et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
JPR, MZ, TB, JT, GME, and CC are inventors of a submitted patent application (WO/2021/098996), which is owned by the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM) and JT. JPR is the CEO and founder of VIAN Therapeutics Inc. MZ and CC are consultants for VIAN Therapeutics. Inc. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

References
-
- Robles JP, Zamora M, Siqueiros-Marquez L, Adan-Castro E, Ramirez-Hernandez G, Nuñez FF, et al.. The HGR motif is the antiangiogenic determinant of vasoinhibin: implications for a therapeutic orally active oligopeptide. Angiogenesis. 2022;25(1):57–70. doi: 10.1007/s10456-021-09800-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

