Protocol for olfactory training in persisting COVID-19-associated loss of smell (SMELL): a monocentric randomised controlled trial conducted in Innsbruck
- PMID: 40436445
- PMCID: PMC12121588
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-094027
Protocol for olfactory training in persisting COVID-19-associated loss of smell (SMELL): a monocentric randomised controlled trial conducted in Innsbruck
Abstract
Introduction: Olfactory dysfunction (OD) following COVID-19 affected up to 70% of patients, with more than 30% still reporting lingering symptoms a year later. Treatment is essential, as previous research has linked (postviral) OD to depression, impaired quality of life (QoL) and even heightened mortality rates.
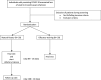
Methods and analysis: We designed a monocentric, single-blinded randomised controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of olfactory training (OT) in individuals with persisting COVID-19-associated loss of smell. Randomisation will be done in a 1:1 manner. OT will be performed using the Sniffin' Sticks Duft Quartett over a period of 12 weeks, two times per day. The primary endpoint of this study is the change in olfactory score between baseline and after 12 weeks, measured by the combined score of the identification and discrimination subscales of the Sniffin' Sticks testing battery. QoL, overall health, mood, personal well-being and symptom severity will be assessed at baseline and during a follow-up visit, using multiple validated questionnaires and scales. OT is offered to the second cohort during an open-label phase extension. This manuscript highlights and discusses the study protocol.
Ethics and dissemination: Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the Ethics Commission of the Medical University of Innsbruck, Austria. Results of this study will be shared through conferences and publications in peer-reviewed journals.
Trial registration number: NCT05421221.
Keywords: COVID-19; Quality of Life; Randomized Controlled Trial.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Financial disclosures for the previous 12 months: BH reports honoraria from Novartis AG, BIAL and AbbVie and grants from the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) outside the submitted work. KS reports honoraria from the International Parkinson and Movement Disorders Society, grants from the FWF Austrian Science Fund, the Michael J. Fox Foundation and the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society, as well as personal fees from Teva, UCB, Lundbeck, AOP Orphan Pharmaceuticals AG, AbbVie, Roche and Grünenthal outside the submitted work. JS received research funds from the R&D Department of MED-EL Elektromedizinische Geräte GmbH, Innsbruck. RH reports honoraria from Integra, Zoll Medical and BD and grants from the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) outside the submitted work. AD reports honoraria from BIAL, Roche, ESAI and Novo Nordisk. All other authors have no competing interest to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
