The key regulator circPDE3B promotes arsenic-induced bladder carcinogenesis by affecting STAT3 and NF-κB stability
- PMID: 40437145
- PMCID: PMC12119782
- DOI: 10.1007/s10565-025-10038-2
The key regulator circPDE3B promotes arsenic-induced bladder carcinogenesis by affecting STAT3 and NF-κB stability
Abstract
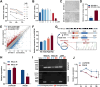
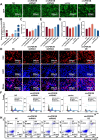
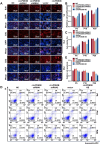
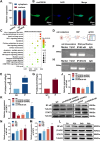
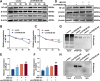
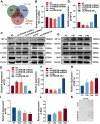
Long-term exposure to arsenic (As), which is a ubiquitous environmental contaminant, significantly enhances the risk of multiple cancers, including bladder and lung cancers. In recent years, the important roles of circular RNAs (circRNAs) in tumorigenesis and development have attracted widespread attention. However, the specific molecular mechanisms by which circRNAs promote bladder cancer development following exposure to arsenic remain incompletely understood. This study is the first to demonstrate that circPDE3B is significantly upregulated in a cell model of transformation triggered by arsenic and that it promotes this transformation process. Our study elucidated the biological function of circPDE3B in vitro, in SV-HUC-1 cells, showing that it accelerates the malignant transformation from arsenic via increasing cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis. Furthermore, we delineated a novel molecular mechanism whereby circPDE3B directly binds to NF-κB and STAT3, inhibiting their ubiquitination and increasing their stability. This, in turn, affects downstream HIF-1α expression, promoting the malignant transformation of SV-HUC-1 cells and eventually resulting in bladder carcinogenesis. Our research reveals the critical regulatory role of circPDE3B in the arsenic-triggered malignant transformation within SV-HUC-1 cells. This study offers broader perspectives on the molecular mechanisms driving bladder cancer progression, while also identifying potential targets for early diagnosis and treatment of bladder tumour.
Keywords: Arsenic; Bladder cancer; NF-κB; STAT3; circPDE3B.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study did not involve the use of human tissue or the performance of animal experiments. Consent for publication: The contents of this manuscript have not been previously published or considered for publication elsewhere. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Arsenic activated GLUT1-mTORC1/HIF-1α-PKM2 positive feedback networks promote proliferation and migration of bladder epithelial cells.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Oct 15;947:174538. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.174538. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38977090
-
Metallothionein 3 Is a Hypoxia-Upregulated Oncogene Enhancing Cell Invasion and Tumorigenesis in Human Bladder Carcinoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 23;20(4):980. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040980. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30813460 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-mediated attenuation of EGLN2 inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway leads to the formation of a loop between HIF-1α and MUC1-C promoting chemoresistance in bladder cancer.Mol Carcinog. 2024 Jul;63(7):1303-1318. doi: 10.1002/mc.23725. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Mol Carcinog. 2024. PMID: 38634741
-
Regulation of Nuclear Factor-KappaB (NF-κB) signaling pathway by non-coding RNAs in cancer: Inhibiting or promoting carcinogenesis?Cancer Lett. 2021 Jul 1;509:63-80. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.03.025. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 33838282 Review.
-
Arsenic-Induced Carcinogenesis: The Impact of miRNA Dysregulation.Toxicol Sci. 2018 Oct 1;165(2):284-290. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfy128. Toxicol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29846715 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amara CS, Kami Reddy KR, Yuntao Y, Chan YS, Piyarathna DWB, Dobrolecki LE, Shih DJH, Shi Z, Xu J, Huang S, Ellis MJ, Apolo AB, Ballester LY, Gao J, Hansel DE, Lotan Y, Hodges HC, Lerner SP, Creighton CJ, Sreekumar A, Zheng WJ, Msaouel P, Kavuri SM, Putluri N. The IL6/JAK/STAT3 signaling axis is a therapeutic vulnerability in SMARCB1-deficient bladder cancer. Nat Commun. 2024;15:1373. 10.1038/s41467-024-45132-2. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Byeon E, Kang HM, Yoon C, Lee JS. Toxicity mechanisms of arsenic compounds in aquatic organisms. Aquat Toxicol. 2021;237:105901. 10.1016/j.aquatox.2021.105901. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Shan G. CircRNA in cancer: Fundamental mechanism and clinical potential. Cancer Lett. 2021;505:49–57. 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.02.004. - PubMed
-
- Dong J, Cheng XD, Zhang WD, Qin JJ. Recent Update on Development of Small-Molecule STAT3 Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy: From Phosphorylation Inhibition to Protein Degradation. J Med Chem. 2021;64:8884–915. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00629. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

