ITIH4 attenuates acute lung injury by Fe-containing particulate matter in mice via Hippo pathway in type II alveolar epithelial cells
- PMID: 40437524
- PMCID: PMC12121068
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-025-03256-z
ITIH4 attenuates acute lung injury by Fe-containing particulate matter in mice via Hippo pathway in type II alveolar epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: Metals in particulate matter (PM), like iron (Fe), were associated with lung injury. Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 (ITIH4) was suggested to inhibit lung inflammation. However, the effect of metals in PM, particularly Fe, on lung inflammation involving ITIH4 remained unclear.
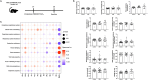
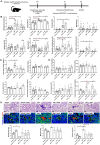
Methods: We investigated the effects of recombinant ITIH4 (rITIH4) against acute lung injury in C57BL/6JNarl and B6.Sftpc-CreERT2;Ai14(RCL-tdT)-D mice exposed to Fe-containing PM. Mice were exposed to diesel exhaust particles (DEP) or soluble iron (FeCl₃) via intratracheal instillation, while rITIH4 treatment was administered intranasally after exposure. Lung function, Fe levels (both bulk and single-cell by inductively-coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and single-cell ICP-MS, respectively), inflammatory cell infiltration, and Hippo pathway regulation in type II alveolar epithelial cells (AECII) were assessed.
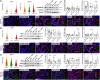
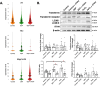
Results: We observed correlation between lung function changes and Fe levels, both in bulk and single-cell Fe in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Single-cell RNA sequencing of the control group identified AECII-related cells characterized by high Sftpc, Sftpa1, Mzb1, B3 gnt5, Cacna1e, and Agbl1 expression. rITIH4 treatment in DEP-exposed mice restored Hippo pathway Cdh1, Itih4, Pdpn, Wwtr1, and Yap1 in AECII. rITIH4 reversed DEP- and Fe-induced increases in neutrophil infiltration, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and monocyte depletion in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). rITIH4 reduced BALF CXCL1/KC levels by DEP and serum 8-isoprostane levels by Fe. rITIH4 also reduced DEP-induced lung damage, increased ⍺-catenin and p-YAP in Fe-exposed mice, and pTAZ/TAZ ratio in both DEP- and Fe-exposed mice. rITIH4 increased pYAP/YAP ratio in DEP-exposed mice while decreasing LC3BII/I ratio in Fe-exposed mice.
Conclusion: ITIH4 attenuated acute lung injury in mice exposed to PM, specifically Fe, by modulating the Hippo pathway in AECII.
Keywords: Air pollution; Autophagy; Diesel exhaust particles; Inflammation; Single-cell analysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal protocols were prepared in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the Laboratory Animal Center at Taipei Medical University (IACUC: LAC-2021–0430) (Taipei, Taiwan). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Manullang A, Chung C-L, Lee Y-L, Yuan T-H, Tran HM, Makrufardi F, Chung KF, Lee K-Y, Chang J-H, Chuang H-C. COPD with Eosinophilic Inflammation is Susceptible to Particulate Air Pollution Exposure. Aerosol Air Qual Res. 2023;23:1–14.
-
- Sun Y, Milando CW, Spangler KR, Wei Y, Schwartz J, Dominici F, Nori-Sarma A, Sun S, Wellenius GA. Short term exposure to low level ambient fine particulate matter and natural cause, cardiovascular, and respiratory morbidity among US adults with health insurance: case time series study. Bmj. 2024;384:e076322 . - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

