GLP-1 receptor agonists and the risk for cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 40437949
- PMCID: PMC12232360
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.16489
GLP-1 receptor agonists and the risk for cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Aims: To assess if there is a difference in the oncogenic risk between GLP-1 RA and comparators in randomized controlled trials.
Materials and methods: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing GLP-1RA to any comparators for diabetes and/or obesity, lasting at least 52 weeks. The endpoints included the incidence of overall cancers and single malignancies.
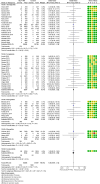
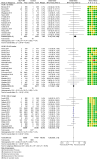
Results: Fifty trials were included. GLP-1RA treatment was not associated with a significant difference in risk for overall cancer (MH-OR 1.05, 95% confidence interval [CI] [0.98, 1.13]). Uterine cancer was significantly reduced in the GLP-1RA arm in trials performed in subjects with obesity (MH-OR 0.24, 95% CI [0.06, 0.94]), but not in those aimed at diabetes treatment (MH-OR 0.92, [0.58, 1.47]). We detected an increase in the risk for thyroid cancer (MH-OR 1.55, [1.05, 2.27]), more evident in longer-term trials, and in the risk for colorectal cancer (MH-OR 1.27 [1.03, 1.57]), which, conversely, was significant only in shorter-term trials. No significant difference in the risk was detected for any other cancer.
Conclusions: GLP-1 RA do not appear to produce an effect on most malignancies in clinical trials. A reduction of very close obesity-associated cancers seems possible, whereas a risk signal for thyroid cancer was observed, prompting the need for further specific studies. On the other hand, the small increase observed in colorectal cancer in shorter-term trials may be the effect of a disproportionate increase in diagnostic procedures in the GLP-1 RA arm, because of the suspicion raised by common side effects of GLP-1 RA.
Keywords: GLP‐1 RA; cancer; dulaglutide; exenatide; glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonists; liraglutide; meta‐analysis; obesity; semaglutide; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2025 The Author(s). Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
GAS has received speaking or consultancy fees from Astra Zeneca, Eli‐Lilly and Novo Nordisk, outside the submitted work. MM has received speaking fees from Astra Zeneca, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Eli‐Lilly, Merck, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi, outside the submitted work. The unit directed by EM has received research grants from Abbott, Eli‐Lilly and Novo Nordisk, outside the submitted work. EM has received consultancy fees or speaking fees from Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Coresearch, Dexcom, Eli‐Lilly, Molteni, Novo Nordisk, Pidkare and Sanofi, outside the submitted work. C.M., G.G.D.V. and C.B. do not have any competing interests to disclose.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

