Selective Glycopolymer Inhibitors of Galectin-3: Supportive Anti-Cancer Agents Protecting Monocytes and Preserving Interferon-Gamma Function
- PMID: 40438186
- PMCID: PMC12118576
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S503381
Selective Glycopolymer Inhibitors of Galectin-3: Supportive Anti-Cancer Agents Protecting Monocytes and Preserving Interferon-Gamma Function
Abstract
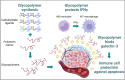
Introduction: The immunosuppressive roles of galectin-3 (Gal-3) in carcinogenesis make this lectin an attractive target for pharmacological inhibition in immunotherapy. Although current clinical immunotherapies appear promising in the treatment of solid tumors, their efficacy is significantly weakened by the hostile immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME). Gal-3, a prominent TME modulator, efficiently subverts the elimination of cancer, either directly by inducing apoptosis of immune cells or indirectly by binding essential effector molecules, such as interferon-gamma (IFNγ).
Methods: N-(2-Hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide (HPMA)-based glycopolymers bearing poly-N-acetyllactosamine-derived tetrasaccharide ligands of Gal-3 were designed, synthesized, and characterized using high-performance liquid chromatography, dynamic light scattering, UV-Vis spectrophotometry, gel permeation chromatography, nuclear magnetic resonance, high-resolution mass spectrometry and CCK-8 assay for evaluation of glycopolymer non-toxicity. Pro-immunogenic effects of purified glycopolymers were tested by apoptotic assay using flow cytometry, competitive ELISA, and in vitro cell-free INFγ-based assay.
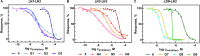
Results: All tested glycopolymers completely inhibited Gal-3-induced apoptosis of monocytes/macrophages, of which the M1 subtype is responsible for eliminating cancer cells during immunotherapy. Moreover, the glycopolymers suppressed Gal-3-induced capture of glycosylated IFNγ by competitive inhibition to Gal-3 carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD), which enables further inherent biological activities of this effector, such as differentiation of monocytes into M1 macrophages and repolarization of M2-macrophages to the M1 state.
Conclusion: The prepared glycopolymers are promising inhibitors of Gal-3 and may serve as important supportive anti-cancer nanosystems enabling the infiltration of proinflammatory macrophages and the reprogramming of unwanted M2 macrophages into the M1 subtype.
Keywords: carbohydrate; galectin-3; glycopolymer; interferon-gamma; monocyte; tumor microenvironment.
© 2025 Filipová et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
High-Affinity N-(2-Hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide Copolymers with Tailored N-Acetyllactosamine Presentation Discriminate between Galectins.Biomacromolecules. 2020 Feb 10;21(2):641-652. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.9b01370. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Biomacromolecules. 2020. PMID: 31904940
-
Cross-Linking Effects Dictate the Preference of Galectins to Bind LacNAc-Decorated HPMA Copolymers.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 1;22(11):6000. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116000. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34206141 Free PMC article.
-
Glycopolymers for Efficient Inhibition of Galectin-3: In Vitro Proof of Efficacy Using Suppression of T Lymphocyte Apoptosis and Tumor Cell Migration.Biomacromolecules. 2020 Aug 10;21(8):3122-3133. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.0c00515. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Biomacromolecules. 2020. PMID: 32697592
-
Galectin-3 inhibitors: a patent review (2008-present).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2014 Oct;24(10):1053-65. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2014.947961. Epub 2014 Aug 9. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2014. PMID: 25109359 Review.
-
Chimera and Tandem-Repeat Type Galectins: The New Targets for Cancer Immunotherapy.Biomolecules. 2023 May 29;13(6):902. doi: 10.3390/biom13060902. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371482 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

