Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles Targeted Delivery System: In Treatment Approach for Dyslipidemia
- PMID: 40438188
- PMCID: PMC12118489
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S517492
Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles Targeted Delivery System: In Treatment Approach for Dyslipidemia
Abstract
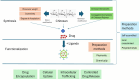
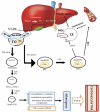
Hyperlipidemia, characterized by abnormally high lipid levels in the bloodstream, is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Conventional treatments have limitations in efficacy and may lead to side effects. Nanotechnology offers unique advantages in drug delivery, including improved drug stability, prolonged circulation time, and enhanced tissue targeting. Using nanoparticles as carriers, therapeutic agents can be precisely delivered to the target site, such as the liver or arterial walls, where lipid metabolism occurs. Chitosan nanoparticles represent an advanced approach engineered with precision to target atherosclerotic plaques. They have dual functionalities, serving therapeutic and diagnostic purposes in managing atherosclerosis. Targeting strategies involve coating nanoparticles with ligands or antibodies that recognize specific receptors overexpressed in hyperlipidemic conditions. This selective uptake maximizes the therapeutic effect while minimizing off-target effects, making it a promising alternative to traditional treatments. The review provides an overview of recent research developments for managing dyslipidemia based on the molecular target pathway of dyslipidemia, focusing on Chitosan-based delivery systems that allow controlled drug release, targeting, and enhancing patient compliance.
Keywords: arterial wall targeting; atherosclerosis; dyslipidemia; hepatic drug targeting; lifestyle modification.
© 2025 Herdiana et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advancing atherosclerosis treatment: Drug encapsulation nanosystems and synthetic HDL nanoparticles.Drug Discov Today. 2025 Jun;30(6):104370. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2025.104370. Epub 2025 May 2. Drug Discov Today. 2025. PMID: 40320132 Review.
-
Delving Into Nanoparticle Systems for Enhanced Drug Delivery Technologies.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025 Mar 4;26(3):74. doi: 10.1208/s12249-025-03063-1. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025. PMID: 40038143 Review.
-
Control of biomedical nanoparticle distribution and drug release in vivo by complex particle design strategies.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2025 Mar;208:114634. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2025.114634. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2025. PMID: 39826847 Review.
-
A comprehensive review on lipid-based nanoparticles via nose to brain targeting as a novel approach.J Microencapsul. 2024 Dec;41(8):681-714. doi: 10.1080/02652048.2024.2404414. Epub 2024 Sep 17. J Microencapsul. 2024. PMID: 39286884 Review.
-
Chitosan Nanoparticles for Targeted Cancer Therapy: A Review of Stimuli-Responsive, Passive, and Active Targeting Strategies.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Aug 15;19:8373-8400. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S472433. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39161363 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

