Gut-brain axis and vascular dementia: a review on mechanisms and Chinese herbal medicine therapeutics
- PMID: 40438206
- PMCID: PMC12116591
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1564928
Gut-brain axis and vascular dementia: a review on mechanisms and Chinese herbal medicine therapeutics
Abstract
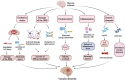
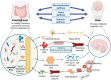
Vascular dementia (VD), the second most prevalent form of dementia among the elderly population, is a cerebrovascular disorder characterized primarily by cognitive impairment. Emerging evidence has revealed that intestinal flora dysbiosis may be implicated not only in gastrointestinal (GI) pathologies but also in central nervous system (CNS) disorders, including VD. The gut-brain axis (GBA) serves as a critical bidirectional pathway through which intestinal flora influences brain physiology and function. Notably, accumulating studies have demonstrated the therapeutic potential of Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) in VD management via modulation of gut microbial composition. This review synthesizes current understanding of the VD- intestinal flora relationship mediated by the GBA, while systematically evaluating evidence for CHM interventions that ameliorate VD through intestinal flora regulation. These insights may offer novel perspectives and methodological approaches for both fundamental research and clinical management of VD.
Keywords: Chinese herbal medicine; gut-brain axis; intestinal flora; pathogenesis; vascular dementia.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Yao, Wang, Lu, Liu, Li, Gong, Cai, Li, Cai and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Understanding the Gut-Brain Axis and Its Therapeutic Implications for Neurodegenerative Disorders.Nutrients. 2023 Oct 31;15(21):4631. doi: 10.3390/nu15214631. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37960284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of gut-brain axis, gut microbial composition, and probiotic intervention in Alzheimer's disease.Life Sci. 2021 Jan 1;264:118627. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118627. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33169684 Review.
-
Traumatic Brain Injury and Gut Microbiome: The Role of the Gut-Brain Axis in Neurodegenerative Processes.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025 Mar 15;25(1):23. doi: 10.1007/s11910-025-01410-0. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40087204 Review.
-
Gut dysbiosis, defective autophagy and altered immune responses in neurodegenerative diseases: Tales of a vicious cycle.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Mar;231:107988. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107988. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34536490 Review.
-
Enteric nervous system dysfunction as a driver of central nervous system disorders: The Forgotten brain in neurological disease.Neuroscience. 2025 Apr 19;572:232-247. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2025.03.015. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Neuroscience. 2025. PMID: 40088964 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

