Analysing the integrated quorum sensing system its potential role in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis
- PMID: 40438239
- PMCID: PMC12116448
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1575421
Analysing the integrated quorum sensing system its potential role in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Analysing the integrated quorum sensing (iqs) system and its potential role in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 11;15:1634997. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1634997. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40568711 Free PMC article.
Abstract
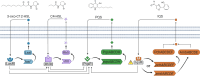
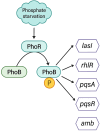
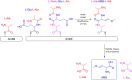
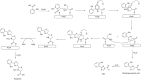
Since its discovery, Quorum Sensing (QS), a form of bacterial communication, has been the focus of numerous studies aimed at unravelling the mechanisms behind this intricate process. Bacterial QS relies on releasing low molecular weight signals known as autoinducers (AIs). When these AIs reach a threshold concentration, they activate coordinated genetic expression of pathogenic and bacterial survival mechanisms. Pseudomonas aeruginosa's QS has been extensively studied due to its incidence and clinical significance in a wide range of human infections. Several decades ago, three QS systems, named Las, Rhl, and Pqs, were identified and have since then become the focus of numerous research studies and the target of innovative diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. However, a fourth QS-related system was more recently proposed that it has been the subject of debate. Named "integrated quorum sensing" (Iqs), interconnects the previously mentioned systems with the phosphate stress response. The associated AI has been identified as 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-thiazole-4-carbaldehyde, also known as IQS. This discovery has sparked a controversial discussion about its biosynthetic origin and whether it truly functions as an intercellular communication system. In this review, we critically discuss the different hypotheses, and its biological relevance while presenting key findings of the Iqs system.
Keywords: IQS; P. aeruginosa; aeruginaldehyde; autoinducers; quorum sensing.
Copyright © 2025 Raya, Montagut and Marco.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alhazmi A. (2015). Pseudomonas aeruginosa – pathogenesis and pathogenic mechanisms. Int. J. Biol. 7, 44-45. doi: 10.5539/ijb.v7n2p44 - DOI
-
- Bielecki P., Jensen V., Schulze W., Godeke J., Strehmel J., Eckweiler D., et al. (2015). Cross talk between the response regulators PhoB and TctD allows for the integration of diverse environmental signals in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, 6413–6425. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv599 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

