Bioactive fraction isolated from Curcuma angustifolia rhizome exerts anti-diabetic effects in vitro, in silico and in vivo by regulating AMPK/PKA signaling pathway
- PMID: 40438603
- PMCID: PMC12116452
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1570533
Bioactive fraction isolated from Curcuma angustifolia rhizome exerts anti-diabetic effects in vitro, in silico and in vivo by regulating AMPK/PKA signaling pathway
Abstract
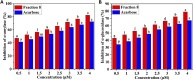
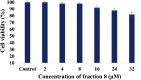
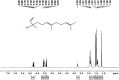
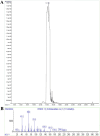
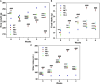
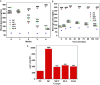
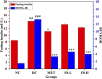
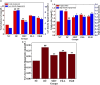
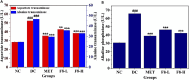
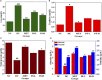
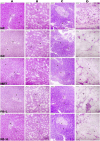
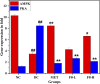
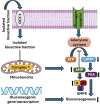
Curcuma angustifolia Roxb. is a therapeutic herb and a member of the Zingiberaceae family. A potential bioactive fraction was isolated from the methanolic extract of Curcuma angustifolia rhizome using column chromatography, and it was characterised using 1H-NMR, GCMS and FTIR analyses. The bioactive fraction showed no toxic effects on the HepG2 cell line and it demonstrated inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase enzymes in vitro with IC50 values of 2.75 ± 0.09 and 4.9 ± 0.07 µM, respectively. Molecular docking analysis also showed that nerolidol, the major constituent of the bioacive fraction inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase enzymes competitively, supporting in vitro antihyperglycemic activity. ADMET analysis showed that nerolidol has the necessary physicochemical parameters for drug-likeness. It also complies with Lipinski's rule, indicating that its chemical structure is appropriate for designing safe and bioavailable oral drug. The antidiabetic efficacy of the isolated bioactive fraction was validated in type 2 diabetic albino wistar rats induced with a high-fat diet and a low dose (35 mg/kg bw) of streptozotocin. After 28 days of intervention, the lower and higher doses of the bioactive fraction (100 and 200 mg/kg BW) substantially decreased fasting blood glucose levels and ameliorated hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, insulin resistance, and hyperlipidemia. The higher dose of bioactive fraction significantly ameliorated liver, kidney, and lipid profiles compared to the standard drug metformin and exhibited lower toxicity in the liver, kidney, pancreas, and epididymal adipose tissue than the lower dose of the bioactive fraction. Gene expression studies revealed that the bioactive fraction upregulated AMPK through downregulating PKA, a mechanism similar to the action of metformin. The results indicate that the isolated bioactive fraction could be a natural alternative to synthetic antidiabetic medications.
Keywords: AMPK; Curcuma angustifolia; PKA; bioactive fraction; molecular docking; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2025 Kavya and Gayathri.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phytochemical Profiling and Assessment of Antidiabetic Activity of Curcuma Angustifolia Rhizome Methanolic Extract: An In Vitro and In Silico Analysis.Chem Biodivers. 2024 May;21(5):e202301788. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202301788. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Chem Biodivers. 2024. PMID: 38484132
-
Phytochemical Composition and Inhibitory Effects of Curcuma angustifolia Leaves Extracts Against α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Enzymes Associated With Hyperglycaemia: In Vitro and In Silico Analysis.Chem Biodivers. 2025 May 27:e00173. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202500173. Online ahead of print. Chem Biodivers. 2025. PMID: 40424639
-
Antidiabetic and antioxidative properties of the hydro-methanolic extract (60:40) of rhizomes of Curcuma amada roxb. (Zingiberaceae) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic male albino rat: a dose-dependent study through biochemical and genomic approaches.J Complement Integr Med. 2019 Jul 18;16(4):/j/jcim.2019.16.issue-4/jcim-2017-0182/jcim-2017-0182.xml. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2017-0182. J Complement Integr Med. 2019. PMID: 31318692
-
Antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic effects of crude fractions and isolated compound from Striga orobanchioides Benth on streptozotocin induced diabetic rats.J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2022 Jul-Sep;13(3):100618. doi: 10.1016/j.jaim.2022.100618. Epub 2022 Aug 26. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2022. PMID: 36030594 Free PMC article.
-
Taxifolin-3-O-glucoside from Osbeckia nepalensis Hook. mediates antihyperglycemic activity in CC1 hepatocytes and in diabetic Wistar rats via regulating AMPK/G6Pase/PEPCK signaling axis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Mar 1;303:115936. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115936. Epub 2022 Nov 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36403743
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

