Safety and Efficacy of Dapagliflozin in Patients With Systemic Right Ventricular Dysfunction: DAPA-SRV Trial
- PMID: 40439149
- PMCID: PMC12229194
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.124.040302
Safety and Efficacy of Dapagliflozin in Patients With Systemic Right Ventricular Dysfunction: DAPA-SRV Trial
Abstract
Background: Heart failure is the leading cause of death in adults with a systemic right ventricle (sRV). While dapagliflozin has proven benefits in patients with acquired heart diseases and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, its impact remains unknown in patients with an sRV. We aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of dapagliflozin in this population.
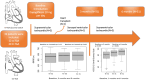
Methods: We conducted a prospective, observational, single-center study including symptomatic patients (New York Health Association [NYHA] functional class ≥2) with sRV dysfunction despite medical treatment, enrolled from February 2023 to February 2024. Patients were assessed at baseline and 3 and 6 months after dapagliflozin introduction. The primary end point was 6-Minute Walk Distance (6MWD). Secondary end points included N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, quality of life (according to the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire-12-item version [KCCQ-12]), NYHA class, systemic and subpulmonary ventricular systolic function, and treatment-related side effects.
Results: A total of 32 patients were included. The mean age of the participants was 48 years (range, 19-79 years), 20 (62%) patients were men, 12 (38%) had congenitally corrected transposition of the great arteries, and 20 (62%) had transposition of the great arteries with atrial switch. At 6 months, 6MWD significantly improved (585 m versus 558 m, P=0.04). Quality of life (91.5 versus 80.5, P<0.001), sRV function (fractional area change: 33% versus 28% [P=0.02]; global longitudinal strain: -13.1% versus -11.2% [P=0.04]) also improved. No significant side effects were observed.
Conclusions: This is the first study, to our knowledge, demonstrating the functional benefits and safety of dapagliflozin in symptomatic patients with sRV dysfunction under medical treatment with sacubitril/valsartan. These results support the need for larger randomized trials to further evaluate this therapeutic option in this population.
Keywords: SGLT2 inhibitor; atrial switch; dapagliflozin; systemic right ventricle; transposition of great arteries.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Comment in
-
Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in Patients With Systemic Right Ventricles: Incrementally Building the Evidence Base.J Am Heart Assoc. 2025 Jun 3;14(11):e043096. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.125.043096. Epub 2025 May 29. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025. PMID: 40439175 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Vejlstrup N, Sørensen K, Mattsson E, Thilén U, Kvidal P, Johansson B, Iversen K, Søndergaard L, Dellborg M, Eriksson P. Long‐term outcome of mustard/Senning correction for transposition of the great arteries in Sweden and Denmark. Circulation. 2015;132:633–638. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.010770 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van Dissel AC, Opotowsky AR, Burchill LJ, Aboulhosn J, Grewal J, Lubert AM, Antonova P, Shah S, Cotts T, John AS, et al. End‐stage heart failure in congenitally corrected transposition of the great arteries: a multicentre study. Eur Heart J. 2023;44:3278–3291. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad511 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albertini M, Santens B, Fusco F, Sarubbi B, Gallego P, Rodriguez‐Puras M‐J, Prokselj K, Kauling RM, Roos‐Hesselink J, Labombarda F, et al. External validation of a risk score model for predicting major clinical events in adults after atrial switch. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024;13:e032174. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.032174 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

