Characterization of Adult and Pediatric Healthcare-Associated and Community-Associated Clostridioides difficile Infections, Canada, 2015-2022
- PMID: 40439410
- PMCID: PMC12123908
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3106.250182
Characterization of Adult and Pediatric Healthcare-Associated and Community-Associated Clostridioides difficile Infections, Canada, 2015-2022
Abstract
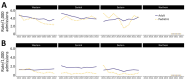
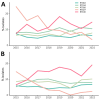
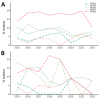
We investigated epidemiologic and molecular characteristics of healthcare-associated (HA) and community-associated (CA) Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) among adult and pediatric patients in Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program hospitals during 2015-2022. Of 30,824 reported CDI cases, 94.9% (29,250/30,824) were among adult (73.2% HA; 26.8% CA) and 5.1% (1,574/30,824) pediatric (77.6% HA; 22.4% CA) patients. During the study period, adult HA CDI rates decreased by 19.9% and CA CDI rates remained stable; pediatric HA CDI rates decreased by 29.6% and CA CDI decreased by 58.3%. Ribotype (RT) 106 was most common among both groups and replaced RT027 as the predominant strain type. RT027 was most associated with adult patients, HA acquisition, severe CDI, and severe outcomes. Moxifloxacin resistance was higher in adult than pediatric cases; clindamycin and rifampin resistance rates were similar between groups. Continued national surveillance is integral to understanding the epidemiology of adult and pediatric CDI in Canada and informing prevention efforts.
Keywords: Canada; Clostridioides difficile; Clostridioides difficile infection; adult CDI; antimicrobial resistance; bacteria; community-associated CDI; enteric infections; healthcare-associated CDI; healthcare-associated infection; nosocomial; pediatric CDI; ribotype.
Figures

References
-
- Katz KC, Golding GR, Choi KB, Pelude L, Amaratunga KR, Taljaard M, et al.; Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program. The evolving epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection in Canadian hospitals during a postepidemic period (2009-2015). CMAJ. 2018;190:E758–65. 10.1503/cmaj.180013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Canadian Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (CARSS). Pan-Canadian action plan on antimicrobial resistance. Ottowa (ON): Public Health Agency of Canada; 2023.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2019. Atlanta: The Centers; 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

