Ethanol induction of FGF21 in the liver is dependent on histone acetylation and ligand activation of ChREBP by glycerol-3-phosphate
- PMID: 40440069
- PMCID: PMC12146743
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2505263122
Ethanol induction of FGF21 in the liver is dependent on histone acetylation and ligand activation of ChREBP by glycerol-3-phosphate
Abstract
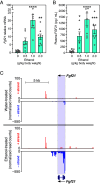
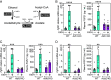
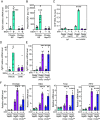
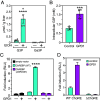
Ethanol rapidly stimulates the liver to synthesize the hormone fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), which then acts on the brain to elicit a multifaceted protective response. We show that in mice, this induction of FGF21 occurs at the level of gene transcription and is regulated by two byproducts of ethanol metabolism, glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P) and acetyl-CoA. Using cell-based reporter and thermal shift binding assays, we show that G3P binds to a conserved domain and activates the transcription factor carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein (ChREBP), which regulates the Fgf21 gene promoter. The stimulation of Fgf21 gene transcription by ethanol also requires its metabolism to acetyl-CoA and correlates with histone acetylation. Accordingly, a p300/CBP histone acetyltransferase inhibitor blocks histone acetylation, ChREBP recruitment, and transcriptional activation at the Fgf21 promoter. Together, these findings reveal a dual regulatory mechanism driven by both G3P and acetyl-CoA that explains ethanol's robust stimulatory effect on Fgf21 and possibly other ChREBP target genes in the liver.
Keywords: ChREBP; FGF21; alcohol; liver; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:Steven Kliewer and David Mangelsdorf are founders and own stock in Atias Pharma.
Figures

Comment in
-
A molecular tango between chromatin and metabolites orchestrates a feedback switch for alcohol consumption.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jul 8;122(27):e2512733122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2512733122. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40587807 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bowland A. C., Melin A. D., Hosken D. J., Hockings K. J., Carrigan M. A., The evolutionary ecology of ethanol. Trends Ecol. Evol. 40, 67–79 (2025). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AA028473/HHS | NIH | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
- R01 DK058110/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA028473/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- I-1275/Welch Foundation (The Welch Foundation)
- DK058110/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

