Unraveling an enhancer-silencer regulatory element showing epistatic interaction with a variant that escaped genome-wide association studies
- PMID: 40441141
- PMCID: PMC12278644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xgen.2025.100889
Unraveling an enhancer-silencer regulatory element showing epistatic interaction with a variant that escaped genome-wide association studies
Abstract
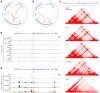
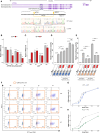
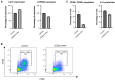
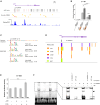
Regulation of gene expression has recently been complicated by identifying Epromoters, a subset of promoters with enhancer function. Here, we uncovered a dual cis-regulatory element, "ESpromoter," exhibiting both enhancer and silencer function as a regulator of the nearby genes ATP2B4 and LAX1 in single human T cells. Through an integrative approach, we pinpointed functional rs11240391, a severe malaria-risk variant that escapes detection in genome-wide association studies, challenging conventional strategies for identifying causal variants. CRISPR-modified cells demonstrated the regulatory effect of ESpromoter and rs11240391 on LAX1 expression and T cell activation. Furthermore, our findings revealed an epistatic interaction between ESpromoter SNPs and rs11240391, impacting severe malaria susceptibility by further reducing LAX1 expression. This groundbreaking discovery challenges the conventional enhancer-silencer dichotomy. It highlights the sophistication of transcriptional regulation and argues for an integrated approach combining genetics, epigenetics, and genomics to identify new therapeutic targets for complex diseases.
Keywords: T cell activation; cis-regulatory elements; dual function; enhancer-silencer; epistatic interaction; functional variants; severe malaria; transcriptional regulation.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Demircioğlu D., Cukuroglu E., Kindermans M., Nandi T., Calabrese C., Fonseca N.A., Kahles A., Lehmann K.-V., Stegle O., Brazma A., et al. A Pan-cancer Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Pervasive Regulation through Alternative Promoters. Cell. 2019;178:1465–1477.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.08.018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sun N., Akay L.A., Murdock M.H., Park Y., Galiana-Melendez F., Bubnys A., Galani K., Mathys H., Jiang X., Ng A.P., et al. Single-nucleus multiregion transcriptomic analysis of brain vasculature in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2023;26:970–982. doi: 10.1038/s41593-023-01334-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Riboldi G.M., Vialle R.A., Navarro E., Udine E., de Paiva Lopes K., Humphrey J., Allan A., Parks M., Henderson B., Astudillo K., et al. Transcriptome deregulation of peripheral monocytes and whole blood in GBA-related Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2022;17:52. doi: 10.1186/s13024-022-00554-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

