Global status and trends of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: A bibliometric study
- PMID: 40441187
- PMCID: PMC12129542
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042603
Global status and trends of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: A bibliometric study
Abstract
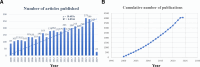
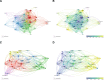
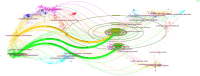
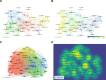
While previous studies have investigated the pathophysiology, epidemiology, and risk factors of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA), research trends and hotspots on this topic remain relatively unexplored. This study aims to develop a visual knowledge map using bibliometric analysis to identify research hotspots and predict future trends in IPA research. A systematic search was conducted on the Web of Science Core Collection for articles published between January 1, 2000, and March 31, 2024. Tools such as CiteSpace and VOSviewer were used to analyze annual publication trends, contributions by countries, institutions, journals, authors, and references, as well as key research areas to identify current hotspots and future directions. A total of 4058 articles were included, representing contributions from 3409 institutions across 749 journals and 214 countries or regions. The United States published the most articles (1312) and emerged as the most influential country in this field. Medical Mycology published the highest number of articles (206), while Clinical Infectious Diseases was the most cited journal (27,450 citations). Keyword clustering revealed 4 major themes: diagnostics (e.g., galactomannan assays), clinical management (e.g., antifungal therapy), at-risk populations (e.g., transplant recipients), and emerging trends (e.g., COVID-19-associated IPA). Temporal analysis identified 3 distinct research phases: early phase (2000-2007): focus on bone marrow transplantation and diagnostic methods. mid-phase (2008-2018): emphasis on clinical guidelines and epidemiological studies. Recent phase (2019-2024): shift toward COVID-19-associated IPA and its impacts. By applying bibliometric methods to analyze IPA research, this study identifies key authors, countries, institutions, and journals in terms of collaboration and influence. It enhances the understanding of research hotspots in the field and provides insights into potential future collaborations and research directions.
Keywords: CiteSpace; VOSviewer; Web of Science Core Collection; bibliometric; invasive pulmonary aspergillosis; research hotspots.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

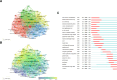

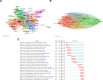
Similar articles
-
Research hotspots and frontiers of machine learning in renal medicine: a bibliometric and visual analysis from 2013 to 2024.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Mar;57(3):907-928. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04259-3. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39472403 Review.
-
Global Highly Cited Publication Trends and Research Hotspots in Osteoporosis and Bone Metabolic Cells: A Bibliometric and Visualization Analysis from 2013 to 2023.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2025;25(5):386-399. doi: 10.2174/0118715303300989240702043834. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 39005119
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Bibliometric analysis of laryngeal cancer treatment literature (2003-2023).Heliyon. 2024 Dec 16;11(1):e40832. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40832. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39811326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and hotspots of Pulmonary Aspergillosis based on web of science.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025 Aug;112(4):116864. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2025.116864. Epub 2025 Apr 20. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40267833
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2020032/The Science and Technology Plan Projects of Qingxiu District of Nanning, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region
- 2019036/The Science and Technology Plan Projects of Qingxiu District of Nanning, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region
- 2023GXNSFBA026024/Youth Science Fund Project of Guangxi Natural Science Foundation
- 2023GXNSFAA026161/Guangxi Natural Science Foundation
- Gui Ke AD22035101/Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Clinical Medical Research Center for Severe Treatment of Major Infectious Diseases
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

