NOX4 as an emerging prognostic and immunological biomarker across pan-cancer analyses
- PMID: 40442199
- PMCID: PMC12123023
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-03499-2
NOX4 as an emerging prognostic and immunological biomarker across pan-cancer analyses
Abstract
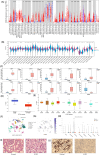
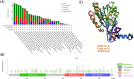
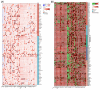
Despite extensive research highlighting the pivotal role of NOX4 in the development of various malignancies, no systematic pan-cancer analysis has been conducted to evaluate its comprehensive prognostic value and potential immunological functions. In this study, we explored the prognostic significance of NOX4 and its role in immune modulation across different cancer types. We performed a pan-cancer analysis of NOX4 expression and its prognostic implications using multiple databases, including TCGA, GEPIA, GTEx, UALCAN, TISCH, GDSC, PDB, TIMER, and cBioPortal. This analysis provided a detailed assessment of NOX4 expression profiles, clinical correlations, genetic variants, tumor microenvironment interactions, immune relevance, therapeutic potential, and related gene functions through various multi-omics approaches. To further investigate these findings, we collected clinical samples from selected cancer types and validated NOX4 expression through immunohistochemistry, H&E staining, and RT-PCR. Our results revealed that NOX4 was overexpressed in most tumors, although its expression was significantly reduced in certain renal cancers. Moreover, we observed distinct correlations between NOX4 expression and patient prognosis. Notably, NOX4 expression was significantly associated with tumor infiltration, indicating its potential as a target for immunotherapy. Additionally, NOX4 expression showed significant correlations with immune checkpoint proteins (ICP), tumor mutation burden (TMB), microsatellite instability (MSI), RNA stemness scores (RNAss), DNA stemness scores (DNAss), RNA methylation, and DNA methylation.
Keywords: Immune microenvironment; NOX4; Pan-cancer; Prognosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Yangjiang People’s Hospital (20210021).
Figures










Similar articles
-
Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis of NOX4 as a biomarker for pan-cancer prognosis and immune infiltration.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Apr 25;16(8):7437-7447. doi: 10.18632/aging.205769. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38663913 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-cancer analysis of NADPH oxidase 4 identifying its prognostic and immunotherapy predictive value and in vitro experimental verification in glioblastoma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Jan 27;146:113815. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113815. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39700959
-
NOX4 serves as a pan-cancer prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in tumorigenesis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 9;15(1):24612. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09690-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40634441 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive pan-cancer analysis reveals prognostic implications of TMEM92 in the tumor immune microenvironment.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Oct;26(10):2701-2717. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03477-6. Epub 2024 Apr 20. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38642258
-
Systematic Pan-Cancer Analysis Identifies TREM2 as an Immunological and Prognostic Biomarker.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 17;12:646523. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.646523. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33679809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung, H. et al. Global Cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin.71 (3), 209–249 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Zou, J. & Wang, E. Cancer biomarker discovery for precision medicine: new progress. Curr. Med. Chem.26 (42), 7655–7671 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

