Plant-based modified cellulose obtained from Populus nigra as a potential adsorbent for pesticides removal from aqueous media
- PMID: 40442246
- PMCID: PMC12122781
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-04084-3
Plant-based modified cellulose obtained from Populus nigra as a potential adsorbent for pesticides removal from aqueous media
Abstract
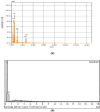
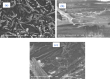
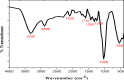
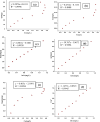
In this study, cellulose was extracted from Populus nigra plant biomass and subsequently modified for use as an adsorbent for the removal of pesticide acetamiprid from wastewater. The extracted cellulose was purified using sodium oxychloride and hydrogen peroxide, acetylated with acetic acid, and further functionalized with polyvinyl alcohol. The prepared adsorbent was characterized via FTIR, UV-Vis spectroscopy, EDX, SEM, and XRD. The effects of various parameters, including the initial concentration of pesticide, adsorbent dosage, contact time, pH, and temperature on adsorption were examined using batch adsorption approaches. Maximum removal was obtained at 80 mg/L pesticide concentration, pH 8, 60 min contact time, and 0.08 g adsorbent dosage. The isothermal data for acetamiprid is matched perfectly to the Freundlich, Temkin and Harkins-Jura isotherm models with regression constant values approaching to 1, whereas good agreement was observed for kinetic data with the pseudo-second-order model. Thermodynamic analysis indicated the adsorption process as favorable and exothermic, with ∆H° = -81.65 kJ/mol, ∆S° = 305.62 J/mol·K, and ∆G° = - 116.90, -150.17 and 180.20 kJ/mol at 293, 313 and 333 K respectively. These findings suggest that the prepared cellulose-based adsorbent is an effective and promising material for pesticide removal from wastewater.
Keywords: Populus nigra; Acetamiprid; Acetylated cellulose; Isothermal study; Kinetic study; Polyvinyl alcohol.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Co-modified MCM-41 as an effective adsorbent for levofloxacin removal from aqueous solution: optimization of process parameters, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Feb;24(6):5238-5248. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-8262-0. Epub 2016 Dec 21. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28004365
-
Preparation of polyethylene grafted cellulose for the removal of diethyl phthalate from wastewater.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Jun;316(Pt 2):144717. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.144717. Epub 2025 May 29. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40449780
-
Removal of Cr(VI) onto Ficus carica biosorbent from water.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2013 Apr;20(4):2632-44. doi: 10.1007/s11356-012-1176-6. Epub 2012 Sep 15. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2013. PMID: 22983603
-
Thermodynamic and kinetic studies of As(V) removal from water by zirconium oxide-coated marine sand.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2013 Aug;20(8):5425-40. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-1543-y. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23423866
-
Adsorption of Pb(II) ions from contaminated water by 1,2,3,4-butanetetracarboxylic acid-modified microcrystalline cellulose: Isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Dec 1;164:3193-3203. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.159. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32853617
References
-
- Plakas, K. V. & Karabelas, A. J. Removal of pesticides from water by NF and RO membranes—A review. Desalination287, 255–265 (2012).
-
- Zolgharnein, J., Shahmoradi, A. & Ghasemi, J. Pesticides removal using conventional and low-cost adsorbents: A review. Clean–Soil Air Water39 (12), 1105–1119 (2011).
-
- Farrukh, S., Hussain, A. & Iqbal, N. Fabrication and characterization of microfiltration blended membranes. Desalin. Water Treat.52 (10–12), 1833–1840 (2014).
-
- Qiu, Y. R. & Mao, L. J. Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by ultrafiltration assisted with copolymer of maleic acid and acrylic acid. Desalination329, 78–85 (2013).
-
- Filipović, K. et al. Highly efficient nano sorbent as a superior material for the purification of wastewater contaminated with anthraquinone dye RB19. J. Water Process. Eng.67, 106118 (2024).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

