Poly(carboxybetaine) lipids enhance mRNA therapeutics efficacy and reduce their immunogenicity
- PMID: 40442447
- PMCID: PMC12354250
- DOI: 10.1038/s41563-025-02240-8
Poly(carboxybetaine) lipids enhance mRNA therapeutics efficacy and reduce their immunogenicity
Abstract
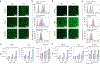
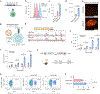
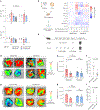
Messenger RNA (mRNA) therapeutics are a promising strategy to combat diverse diseases. Traditional lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations for mRNA delivery contain poly(ethylene) glycol (PEG), a polymer widely used in drug delivery carriers but that recently has been associated with efficacy and immunogenicity concerns. Here we report poly(carboxybetaine) (PCB) lipids as surrogates for PEG-lipids used in mRNA formulations. In vitro studies with immortalized and primary cells show that PCB-containing LNPs have higher mRNA transfection efficiency than PEG-containing LNPs across different formulations. Moreover, primary cell engineering and in vivo immunization studies in mice further demonstrate greater therapeutic efficacy of PCB-containing LNPs over their PEG counterparts. Mechanistic assays show that this improvement is attributed to enhanced endosomal escape of PCB-containing LNPs. These formulations exhibit a safe immunotoxicity profile and effectively mitigate the accelerated blood clearance effect that has been observed for PEG-containing LNPs, enabling repeated administrations without efficacy loss. Overall, these findings highlight PCB-containing LNPs as a potent and safe mRNA delivery platform for clinical applications.
© 2025. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S. Luozhong, P.L., Z.Y. and S.J. are authors of a patent application related to this work (PCT/US2021/064639) filed by Cornell University in the United States. S. Luozhong, R. Li, P.L. and S.J. are authors of a patent related to this work (PCT/US2024/048135) filed by Cornell University in the United States. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Mullard A COVID-19 vaccine success enables a bolder vision for mRNA cancer vaccines, says BioNTech CEO. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 20, 500–501 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Akinc A et al. The Onpattro story and the clinical translation of nanomedicines containing nucleic acid-based drugs. Nat. Nanotechnol 14, 1084–1087 (2019). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

