Phage/nanoparticle cocktails for a biocompatible and environmentally friendly antibacterial therapy
- PMID: 40442509
- PMCID: PMC12122614
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-025-13526-x
Phage/nanoparticle cocktails for a biocompatible and environmentally friendly antibacterial therapy
Abstract
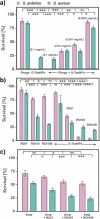
Antibiotic resistance continues to rise, necessitating alternative strategies. Bacteriophages have emerged as promising natural antibacterial agents, offering a targeted approach to combating bacterial infections. Combining bacteriophages with nanoparticles presents a novel approach that could enhance antibacterial potency while reducing the risk of resistance. While phage/antibiotic cocktails are widely explored to enhance antibacterial efficacy and prevent resistance, research on phage/nanoparticle combinations remains limited. We explore the synergy between green tea extract-capped silver nanoparticles (G-TeaNPs) and bacteriophages in combating pathogenic bacteria (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella enterica). G-TeaNPs show minimal antiphage activity, ensuring compatibility in phage-NP formulations. These combinations significantly reduce bacterial counts in a short time (only 3 h), e.g., S. aureus survival is around 30% after incubation with just 0.001 mg/mL of G-TeaNPs, while G-TeaNPs and phages alone result in around 80% and 70% survival, respectively. Cytotoxicity tests against eukaryotic 3T3 NIH fibroblast cells confirm biocompatibility at effective concentrations. Additionally, we examine G-TeaNPs' impact on the free-living protist Acanthamoeba castellanii. Both green tea extract and G-TeaNPs can reduce A. castellanii cell counts by 80%, but only at high concentrations. Microscopy revealed nanoparticle uptake by amoebae, causing intracellular accumulation and vacuolization, while green tea extract induced similar changes without uptake. Our findings highlight G-TeaNPs as safe, effective agents in phage/nanoparticle antibacterial formulations with dual antimicrobial and amoebicidal properties for therapeutic and environmental applications. KEYPOINTS: • Silver nanoparticles synthesized with tea extracts (G-TeaNPs) have a minimal effect on the tested viruses. • Combining G-TeaNP with bacteriophages offers new-generation antibacterial cocktails. • Green tea extracts and AgNPs present concentration-dependent anti-amoebic activity.
Keywords: Acanthamoeba castellanii; Antimicrobial agents; Antimicrobial combinations; Bacteriophages; Silver nanoparticles.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A silver lining in MRSA treatment: The synergistic action of poloxamer-stabilized silver nanoparticles and methicillin against antimicrobial resistance.Microb Pathog. 2024 Dec;197:107087. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.107087. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39481693
-
Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Prepared from Camellia Sinensis Extracts in Multi-Drug Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2024 Nov 11;58(6):659-676. doi: 10.33594/000000741. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39535105
-
The effect of coffee as a bio reductant in the synthesis of silver nano particles combined with laser photodynamics for bacteria inactivation.Braz J Biol. 2025 May 2;85:e288042. doi: 10.1590/1519-6984.288042. eCollection 2025. Braz J Biol. 2025. PMID: 40332206
-
A new strategy to achieve high antimicrobial activity: green synthesised silver nanoparticle formulations with Galium aparine and Helichrysum arenarium.Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2023 Jun 26;74(2):90-98. doi: 10.2478/aiht-2023-74-3684. eCollection 2023 Jun 1. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2023. PMID: 37357883 Free PMC article.
-
A promising agent against wild-type and antibiotic-resistant bacteria using biogenic silver nanoparticles from Marphysa moribidii extract.Microb Pathog. 2025 Jul;204:107582. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2025.107582. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Microb Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40222565
References
-
- Abdelsattar AS, Yakoup AY, Khaled Y, Safwat A, El-Shibiny A (2023) The synergistic effect of using bacteriophages and chitosan nanoparticles against pathogenic bacteria as a novel therapeutic approach. Int J Biol Macromol 228:374–384. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.246 - PubMed
-
- Agnihotri S, Mukherji S, Mukherji S (2014) Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5–100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv 4:3974–3983. 10.1039/c3ra44507k
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

