Assessment of the association between C2 vertebral morphology and facial asymmetry using CBCT and panoramic radiography
- PMID: 40442617
- PMCID: PMC12123825
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-025-01744-8
Assessment of the association between C2 vertebral morphology and facial asymmetry using CBCT and panoramic radiography
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the relationship between the morphology of the Axis (C2 vertebra) and facial asymmetry using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and panoramic radiographs.
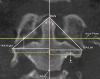
Materials and methods: A retrospective evaluation was performed on CBCT and panoramic radiographs of 50 patients (aged 18-45 years) selected from university archives. Axis vertebral morphology was assessed on CBCT using angular and perpendicular measurements of the dens and transverse processes. Facial asymmetry was evaluated on panoramic radiographs by measuring bilateral distances and angles from the condylion to the midsagittal plane. Pearson's correlation and Chi-square tests were used to analyze associations. Sample size was calculated based on a priori power analysis.
Results: Moderate but statistically significant correlations were identified between specific vertebral and facial asymmetry parameters. A negative correlation was observed between the right Axis angle and the right Co-ANSMe perpendicular distance (r = - 0.31, p = 0.026), while the left Axis perpendicular distance showed a positive correlation with both right (r = 0.36, p = 0.009) and left (r = 0.33, p = 0.018) Co-ANSMe perpendicular distances. Additionally, combined measurements of Axis and Co-ANSMe distances demonstrated a moderate positive correlation (r = 0.31, p = 0.028). No other statistically significant correlations were found.
Conclusions: Morphological differences in the Axis vertebra appear moderately associated with transverse facial asymmetry. These findings may offer additional reference points for radiographic assessment. Further studies with larger samples are recommended to confirm these observations.
Keywords: Anterior nasal spine; Cervical vertebra; Cone-beam computed tomography; Facial asymmetry; Panoramic radiograph.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Kocaeli University Non-Interventional Clinical Research Ethics Committee (Protocol code: GOKAEK-2024/05.15). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants whose data were included in this retrospective analysis. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reliability and validity of mandibular posterior vertical asymmetry index in panoramic radiography compared with cone-beam computed tomography.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2018 Apr;153(4):558-567. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2017.08.019. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2018. PMID: 29602348
-
Cone beam computed tomography evaluation of the relationship between atlantodental interval and skeletal facial morphology in adolescents.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Nov-Dec;86(6):711-719. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2019.05.005. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 31285185 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of digital panoramic radiography versus cone beam computerized tomography for measuring alveolar bone.Head Face Med. 2017 Feb 22;13(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13005-017-0135-3. Head Face Med. 2017. PMID: 28228135 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the relationship between appearances of the lingual foramen on panoramic radiography and cone-beam computed tomography.Niger J Clin Pract. 2020 Feb;23(2):205-211. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_377_19. Niger J Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 32031095
-
Statistical shape analysis-based determination of optimal midsagittal reference plane for evaluation of facial asymmetry.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2016 Aug;150(2):252-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.01.017. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2016. PMID: 27476357
References
-
- Sezgin OS, Celenk P, Arici S. Mandibular asymmetry in different occlusion patterns. Angle Orthod. 2007;77:803–7. 10.2319/092506-392. - PubMed
-
- Bebnowski D, Hänggi MP, Markic G, Roos M, Peltomäki T. Cervical vertebrae anomalies in subjects with class II malocclusion assessed by lateral cephalogram and cone beam computed tomography. Eur J Orthod. 2012;34:226–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

