Evaluating the impact of metabolic indicators and scores on cardiovascular events using machine learning
- PMID: 40442740
- PMCID: PMC12123715
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-025-01753-1
Evaluating the impact of metabolic indicators and scores on cardiovascular events using machine learning
Abstract
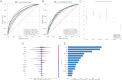
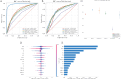
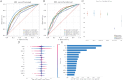
Cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, and heart failure impact millions of people annually globally and are a major cause of disease and death. This study explores the predictive capabilities of novel metabolic indices (TyG, HOMA-IR, TG/HDL-C, and VAI) for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and analyzes their relationships with diabetes and cardiovascular risks. Using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) spanning from 2003 to 2018, we applied multiple machine learning algorithms to evaluate nine metabolic indicators including cholesterol levels, triglycerides, insulin, and waist circumference. Through cross-validation to validate model performance, the XGBoost algorithm demonstrated the most accurate performance in predicting cardiovascular outcomes, particularly for diseases like angina and heart failure. Additionally, SHAP value analysis confirmed the critical roles of waist circumference and METS-IR in predicting adverse cardiovascular events. Furthermore, we employed 100 machine learning algorithms to calculate the AUC values of metabolic indicators in predicting AP, CHD, HF, and MI, showing that METS-IR had the greatest contribution in these aspects. This research highlights the significance of metabolic indices in stratifying cardiovascular risks and presents potential avenues for targeted preventive strategies.
Keywords: Angina pectoris; Coronary disease; Heart failure; Metabolism; Myocardial infarction.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Kloner RA, Chaitman B. Angina and its management. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2017;22(3):199–209. - PubMed
-
- Katta N, Loethen T, Lavie CJ, Alpert MA. Obesity and coronary heart disease: epidemiology, pathology, and coronary artery imaging. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2021;46(3): 100655. - PubMed
-
- Gulati R, Behfar A, Narula J, Kanwar A, Lerman A, Cooper L, Singh M. Acute myocardial infarction in young individuals. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(1):136–56. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

