Enhancing systemic lupus erythematosus treatment outcomes with an early initiation of belimumab: insights from a multicenter retrospective study within the first five years
- PMID: 40442811
- PMCID: PMC12121007
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-025-03581-0
Enhancing systemic lupus erythematosus treatment outcomes with an early initiation of belimumab: insights from a multicenter retrospective study within the first five years
Abstract
Background: The human monoclonal antibody belimumab (BEL) has emerged as a promising treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), particularly for reducing the need for glucocorticoids and minimizing organ damage. The optimal timing of BEL initiation has been unclear; emerging evidence suggests that early intervention with BEL, particularly within the first 5 years of diagnosis, may yield better outcomes by modulating disease progression and reducing flare frequency. Understanding the relationship between disease duration and BEL efficacy is essential for the development of tailored strategies.
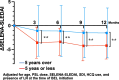
Patients and methods: We analyzed patients with SLE treated at our hospital and associated facilities who were diagnosed according to the 1997 ACR or 2012 SLICC criteria and who began BEL treatment between December 2017 and August 2021. Patients who were followed for ≥ 12 months after BEL initiation were included. We investigated the changes in the patients' Safety of Estrogens in Lupus National Assessment-Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SELENA-SLEDAI) scores at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months after the introduction of BEL, comparing patients with disease durations ≤ 5 years to those with > 5 years. A mixed-effects model was adjusted for the patients' ages, prednisolone dosages, initial SELENA-SLEDAI scores, Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) damage index (SDI), hydroxychloroquine use, and lupus nephritis. Clinical manifestations including arthritis, skin lesions, and hematological abnormalities were monitored to assess the broader impacts of BEL.
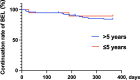
Results: One hundred eleven patients were initially registered; among them, 97 patients were included in the final analysis. The study population (mean age, 41 years; mean SELENA-SLEDAI, 7 points; 51% using hydroxychloroquine) included 19 patients with a ≤ 5-year SLE duration and 78 with SLE durations > 5 years. The baseline SELENA-SLEDAI scores were higher in the ≤ 5-year group (p = 0.047), indicating more active disease. Patients with ≤ 5 years of disease had significantly greater improvements in SELENA-SLEDAI scores at 6, 9, and 12 months (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: These results highlight the importance of early BEL initiation in SLE, demonstrating that patients with shorter disease durations achieve more substantial improvements in disease activity with early BEL treatment. Our findings also reveal the potential benefits of early BEL intervention and suggest that incorporating the disease duration into treatment decisions may optimize patient outcomes.
Keywords: B cell therapy; Belimumab; Disease duration; Early intervention; SELENA-SLEDAI; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was performed in accord with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Investigation and Ethics Committee at Nagasaki University Hospital (approval no. 19102116–6). The patients gave their informed consent to be subjected to the protocol. Consent for publication: Some of the patients provided written informed consent for the use and publications of their data, and the opt-out strategy was used by the remainder of the patients. Competing interests: KI has received speaker honoraria from AbbVie GK, Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation, AstraZeneca K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., GlaxoSmithKline K.K. (GSK), Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. MU has received honoraria from AbbVie GK, Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation, AstraZeneca K.K., and GlaxoSmithKline K.K. (GSK). TS has received honoraria from AstraZeneca K.K. and GlaxoSmithKline K.K. (GSK). AK has received honoraria from AbbVie GK, Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Pfizer, and Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Tsokos GC. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(22):2110–21. - PubMed
-
- Gatto M, Zen M, Iaccarino L, Doria A. New therapeutic strategies in systemic lupus erythematosus management. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(1):30–48. - PubMed
-
- Mockel T, Basta F, Weinmann-Menke J, Schwarting A. B cell activating factor (BAFF): Structure, functions, autoimmunity and clinical implications in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Autoimmun Rev. 2021;20(2):102736. - PubMed
-
- Gatto M, Saccon F, Zen M, Regola F, Fredi M, Andreoli L, Tincani A, Urban ML, Emmi G, Ceccarelli F, et al. Early disease and low baseline damage as predictors of response to belimumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in a real-life setting. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(8):1314–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

