Multimeric Conjugates Using Engineered Peptide Scaffolds for Efficient siRNA Delivery
- PMID: 40443118
- PMCID: PMC12183678
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5c00156
Multimeric Conjugates Using Engineered Peptide Scaffolds for Efficient siRNA Delivery
Abstract
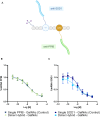
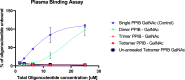
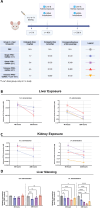
Oligonucleotide therapeutics (ONT) traditionally involve a single targeting moiety per oligonucleotide when conjugated for organ delivery. Multimerization represents a novel approach by connecting multiple ONTs to a single scaffold, thereby influencing the drug's activity and biophysical properties in vivo. Recently, others have demonstrated the efficacy of this strategy, showing enhanced tissue retention and extended silencing with the capability to target multiple genes simultaneously. The investigation of diverse multimeric designs is thus an exciting opportunity to explore the delivery of the ONT. In this study, we engineered a versatile peptide branching unit able to link up to four small interfering RNAs together. We conjugated a GalNAc targeting moiety to these scaffolds for liver hepatocyte delivery and assessed their silencing activity. Our approach was further expanded to explore different peptide architectures (linear versus cyclized) and additional functionalities, including endosomal escape domains and dual target silencing. We then evaluated the constructs via subcutaneous and intravenous (i.v.) administration in mice. Notably, the intravenous administration of multimeric siRNA GalNAc demonstrated potent silencing in the liver and significantly affected liver-to-kidney biodistribution. Our findings suggest that peptides as branching units offer a promising pathway for ONT multimerization, advancing the challenges of drug delivery.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparative metabolism of an N-acetylgalactosamine-conjugated small interfering RNA, inclisiran, among various in vitro systems and correlations with in vivo metabolism in rats.Drug Metab Dispos. 2025 Jun;53(6):100089. doi: 10.1016/j.dmd.2025.100089. Epub 2025 Apr 29. Drug Metab Dispos. 2025. PMID: 40505270
-
GalNAc-siRNA conjugates mediate the silencing of the parasite-derived lncRNA: A novel therapeutic approach for liver fluke-induced liver fibrosis.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Aug;319(Pt 2):145580. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.145580. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40581025
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Maternal and neonatal outcomes of elective induction of labor.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2009 Mar;(176):1-257. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2009. PMID: 19408970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Østergaard M. E., Jackson M., Low A., Chappell A. E., Lee R. G., Peralta R. Q., Yu J., Kinberger G. A., Dan A., Carty R., Tanowitz M., Anderson P., Kim T.-W., Fradkin L., Mullick A. E., Murray S., Rigo F., Prakash T. P., Bennett C. F., Swayze E. E., Gaus H. J., Seth P. P.. Conjugation of Hydrophobic Moieties Enhances Potency of Antisense Oligonucleotides in the Muscle of Rodents and Non-Human Primates. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(12):6045–6058. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz360. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

