Factors determining chromosomal localization of transposable elements in plants
- PMID: 40443126
- PMCID: PMC12477314
- DOI: 10.1111/plb.70057
Factors determining chromosomal localization of transposable elements in plants
Abstract
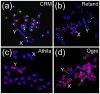
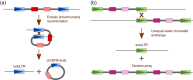
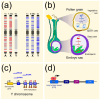
Transposable elements (TEs) constitute a significant part of plant genomes and shape their genomic landscape. While some TEs are ubiquitously dispersed, other elements specifically occupy discrete genomic loci. The evolutionary forces behind the chromosomal localization of TEs are poorly understood. Therefore, we first review specific chromosomal niches where TEs are often localized including (i) centromeres, (ii) (sub)telomeres, (iii) genes, and (iv) sex chromosomes. In the second part of this review, we focus on the processes standing behind non-equal distribution of various TEs in genomes including (i) purifying selection, (ii) insertion site preference or targeting of TEs, (iii) post-insertion ectopic recombination between TEs, and (iv) spatiotemporal regulation of TE jumping. Using the combination of the above processes, we explain the distribution of TEs on sex chromosomes. We also describe the phenomena of mutual nesting of TEs, epigenetic mark silencing in TEs, and TE interactions in the 3D interphase nucleus concerning TE localization. We summarize the functional consequences of TE distribution and relate them to cell functioning and genome evolution.
Keywords: Centromere; chromosomes; plant genome; recombination; transcription factor; transposable elements.
© 2025 The Author(s). Plant Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of German Society for Plant Sciences, Royal Botanical Society of the Netherlands.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmed H.I., Heuberger M., Schoen A., Koo D.H., Quiroz‐Chavez J., Adhikari L., Raupp J., Cauet S., Rodde N., Cravero C., Callot C., Lazo G.R., Kathiresan N., Sharma P.K., Moot I., Yadav I.S., Singh L., Saripalli G., Rawat N., Datla R., Athiyannan N., Ramirez‐Gonzalez R.H., Uauy C., Wicker T., Tiwari V.K., Abrouk M., Poland J., Krattinger S.G. (2023) Einkorn genomics sheds light on history of the oldest domesticated wheat. Nature, 620, 830–838. 10.1038/s41586-023-06389-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

