Eupatilin unveiled: An in-depth exploration of research advancements and clinical therapeutic prospects
- PMID: 40443403
- PMCID: PMC12116271
- DOI: 10.1515/jtim-2025-0016
Eupatilin unveiled: An in-depth exploration of research advancements and clinical therapeutic prospects
Abstract
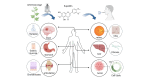
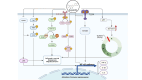
Eupatilin, a flavonoid found in Artemisia argyi (Compositae) leaves, exhibits robust anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-tumor properties. Numerous investigations have demonstrated remarkable efficacy of eupatilin across various disease models, spanning digestive, respiratory, nervous, and dermatological conditions. This review aims to provide an overview of recent studies elucidating the mechanistic actions of eupatilin across a spectrum of disease models and evaluate its clinical applicability. The findings herein provide valuable insights for advancing the study of novel Traditional Chinese Medicine compounds and their clinical utilization.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory properties; antitumor properties; clinical trials; eupatilin; immunoregulation; pharmacological activities.
© 2025 Zheng Li, Xiumei Wang, Ksenija Tasich, David Hike, Jackson G. Schumacher, Qingju Zhou, Weitao Man, Yong Huang, published by De Gruyter on behalf of the SMP.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest All authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Butler MS. Natural products to drugs: natural product-derived compounds in clinical trials. Nat Prod Rep. 2008;25:475–516. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
