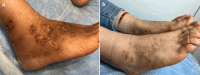
Effective Treatment of Livedoid Vasculopathy With Oral Tofacitinib
- PMID: 40443500
- PMCID: PMC12119902
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.70536
Effective Treatment of Livedoid Vasculopathy With Oral Tofacitinib
Abstract
We present a woman with severe refractory livedoid vasculopathy who was successfully treated with tofacitinib (5 mg twice a day). The ulcers gradually healed over a period of 2-3 months without experiencing any adverse events over a 1-year follow-up period. Tofacitinib may be considered a safe and effective therapy for patients with livedoid vasculopathy.
Keywords: JAK inhibitors; baricitinib; livedoid vasculopathy; tofacitinib.
© 2025 The Author(s). Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that none of the authors listed on the manuscript are employed by a government agency that has a primary function other than research and/or education. None of the authors submitting this manuscript are acting as an official representative or on behalf of the government.The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kerk N. and Goerge T., “Livedoid Vasculopathy – Current Aspects of Diagnosis and Treatment of Cutaneous Infarction,” Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft 11, no. 5 (2013): 407–410. - PubMed
-
- Vasudevan B., Neema S., and Verma R., “Livedoid Vasculopathy: A Review of Pathogenesis and Principles of Management,” Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology 82, no. 5 (2016): 478–488. - PubMed
-
- Micieli R. and Alavi A., “Treatment for Livedoid Vasculopathy: A Systematic Review,” JAMA Dermatology 154, no. 2 (2018): 193–202. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources