Lactylation: From Homeostasis to Pathological Implications and Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 40443721
- PMCID: PMC12122191
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.70226
Lactylation: From Homeostasis to Pathological Implications and Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
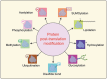
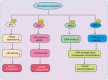
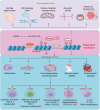
Lactylation, a recently identified post-translational modification, represents a groundbreaking addition to the epigenetic landscape, revealing its pivotal role in gene regulation and metabolic adaptation. Unlike traditional modifications, lactylation directly links metabolic intermediates, such as lactate, to protein function and cellular behavior. Emerging evidence highlights the critical involvement of lactylation in diverse biological processes, including immune response modulation, cellular differentiation, and tumor progression. However, its regulatory mechanisms, biological implications, and disease associations remain poorly understood. This review systematically explores the enzymatic and nonenzymatic mechanisms underlying protein lactylation, shedding light on the interplay between cellular metabolism and epigenetic control. We comprehensively analyze its biological functions in normal physiology, such as immune homeostasis and tissue repair, and its dysregulation in pathological contexts, including cancer, inflammation, and metabolic disorders. Moreover, we discuss advanced detection technologies and potential therapeutic interventions targeting lactylation pathways. By integrating these insights, this review aims to bridge critical knowledge gaps and propose future directions for research. Highlighting lactylation's multifaceted roles in health and disease, this review provides a timely resource for understanding its clinical implications, particularly as a novel target for precision medicine in metabolic and oncological therapies.
Keywords: biological significance; cancer immunotherapy; pathology; physiology; protein lactylation.
© 2025 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ye L., Jiang Y., and Zhang M., “Crosstalk Between Glucose Metabolism, Lactate Production and Immune Response Modulation,” Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews 68 (2022): 81–92. - PubMed
-
- Li X., Yu T., Li X., He X., Zhang B., and Yang Y., “Role of Novel Protein Acylation Modifications in Immunity and Its Related Diseases,” Immunology 173, no. 1 (2024): 53–75. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
