Carbon-sequestration gradient insulation composites
- PMID: 40444255
- PMCID: PMC12122010
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2024.102222
Carbon-sequestration gradient insulation composites
Abstract
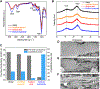
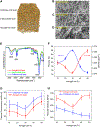
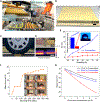
The massive use of carbon-sequestration building materials promises a potential global carbon sink in decarbonizing the building industry. Renewable biogenic materials from abundant agriculture waste for building practice have been around over thousands of years. However, in addition to their flammability and moisture problems, addressing their low thermal and structural performance is also becoming indispensable and urgent when it comes to environmentally sustainable and energy-efficient buildings. Here, we report a nature-inspired biogenic gradient insulation composite with an optimized silica concentration of 30 wt %, a density of 0.246 g/cm3, and a porosity of 86%. The gradient hybrid composite exhibits a thermal conductivity of 28.2 mW m-1 K-1, which is the lowest achieved under optimal preparation conditions. It also shows a flexural modulus of 590 MPa for the aerogel-rich layer without surface modification, and it demonstrates superior fire retardancy and superhydrophobicity after surface treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


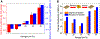
References
-
- van Ewijk S, Stegemann JA, and Ekins P (2020). Limited climate benefits of global recycling of pulp and paper. Nat. Sustain 4, 180–187. 10.1038/s41893-020-00624-z. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
