Modern therapeutic approaches for hepatic tumors: progress, limitations, and future directions
- PMID: 40445470
- PMCID: PMC12125458
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02773-z
Modern therapeutic approaches for hepatic tumors: progress, limitations, and future directions
Abstract
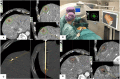
Hepatic tumors, such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and metastatic liver malignancies, represent a substantial worldwide health concern due to elevated mortality rates and unfavorable prognoses. Notwithstanding progress in surgical, locoregional, and systemic therapy, significant obstacles like as late-stage diagnosis, treatment resistance, and discrepancies in healthcare access still hinder patient outcomes. This study thoroughly analyzes recent breakthroughs in hepatic tumor treatment, including surgical improvements, immunotherapy, targeted medicines, and nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems. The discourse emphasizes minimally invasive methods including laparoscopic and robotic-assisted hepatectomies, the function of immune checkpoint inhibitors, and the promise of nanoparticle-based therapeutics to improve drug administration while reducing systemic toxicity. This study aims to critically assess current hepatic tumor treatments, examining their effectiveness, constraints, and prospective developments. Critical concerns, such as drug resistance, post-treatment recurrence, and the accessibility of innovative medicines in resource-constrained environments, are addressed. The review underscores the significance of personalized medicine, biomarker-guided treatment approaches, and interdisciplinary teamwork in enhancing therapeutic results. Future research seeks to enhance patient survival and quality of life through the integration of developing technology and the refinement of present treatment approaches.
Keywords: Hepatic tumors; Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); Immunotherapy; Liver cancer treatment; Nanotechnology; Surgical innovations.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
