Gene editing of the E3 ligase PIRE1 fine-tunes reactive oxygen species production for enhanced bacterial disease resistance in tomato
- PMID: 40445949
- PMCID: PMC12124405
- DOI: 10.1093/plcell/koaf049
Gene editing of the E3 ligase PIRE1 fine-tunes reactive oxygen species production for enhanced bacterial disease resistance in tomato
Abstract
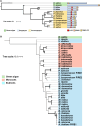
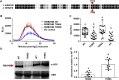
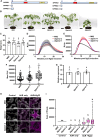
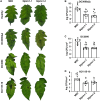
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation is required for effective plant defense. Accumulation of the Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) NADPH oxidase respiratory burst oxidase homolog D (RBOHD) is regulated by phosphorylation of a conserved C-terminal residue (T912) leading to ubiquitination by the RING E3 ligase Pbl13-interacting RING domain E3 ligase (PIRE). Arabidopsis PIRE knockouts exhibit enhanced ROS production and resistance to the foliar pathogen Pseudomonas syringae. Here, we identified 170 PIRE homologs, which emerged in tracheophytes and expanded in angiosperms. We investigated the role of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) PIRE homologs in regulating ROS production, RBOH stability, and disease resistance. Mutational analyses of residues corresponding to T912 in the tomato RBOHD ortholog, SlRBOHB, affected protein accumulation and ROS production in a PIRE-dependent manner. Using genome editing, we generated mutants in 2 S. lycopersicum PIRE (SlPIRE) homologs. SlPIRE1 edited lines (Slpire1) in the tomato cultivar M82 displayed enhanced ROS production upon treatment with flg22, an immunogenic epitope of flagellin. Furthermore, Slpire1 exhibited decreased disease symptoms and bacterial accumulation when inoculated with foliar bacterial pathogens P. syringae and Xanthomonas campestris. However, Slpire1 exhibited similar levels of colonization as wild type upon inoculation with diverse soil-borne pathogens. These results indicate that PIRE regulates RBOHs in multiple plant species and is a promising target for foliar disease control. This study also highlights the pathogen-specific role of PIRE, indicating its potential for targeted manipulation to enhance foliar disease resistance without affecting root-associated pathogenic interactions.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society of Plant Biologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
Figures

Update of
-
Gene editing of the E3 ligase PIRE1 fine-tunes ROS production for enhanced bacterial disease resistance in tomato.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 3:2024.07.31.606097. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.31.606097. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Plant Cell. 2025 May 9;37(5):koaf049. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koaf049. PMID: 39131268 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Gene editing of the E3 ligase PIRE1 fine-tunes ROS production for enhanced bacterial disease resistance in tomato.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 3:2024.07.31.606097. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.31.606097. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Plant Cell. 2025 May 9;37(5):koaf049. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koaf049. PMID: 39131268 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Regulation of reactive oxygen species during plant immunity through phosphorylation and ubiquitination of RBOHD.Nat Commun. 2020 Apr 15;11(1):1838. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15601-5. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32296066 Free PMC article.
-
CRK2 and C-terminal Phosphorylation of NADPH Oxidase RBOHD Regulate Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2020 Apr;32(4):1063-1080. doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00525. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Plant Cell. 2020. PMID: 32034035 Free PMC article.
-
Histone variant H2A.Z is a conserved regulator of RBOH expression and ROS production during innate immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana and Solanum lycopersicum.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Apr 9;757:151618. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.151618. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40101652
-
Effector-triggered immunity mediated by the Pto kinase.Trends Plant Sci. 2011 Mar;16(3):132-40. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.11.001. Epub 2010 Nov 26. Trends Plant Sci. 2011. PMID: 21112235 Review.
Cited by
-
Focus on Translational Research from Arabidopsis to Crop Plants and Beyond.Plant Cell. 2025 May 9;37(5):koaf119. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koaf119. Plant Cell. 2025. PMID: 40373203 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Akter A, Hassan L, Nihad SAI, Hasan MJ, Robin AHK, Khatun M, Tabassum A, Latif MA. Pyramiding of bacterial blight resistance genes into promising restorer BRRI31R line through marker-assisted backcross breeding and evaluation of agro-morphological and physiochemical characteristics of developed resistant restorer lines. PLoS One. 2024:19(6):e0301342. 10.1371/journal.pone.0301342 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

