Decentralized TB diagnostic testing with Truenat MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx vs. hub-and-spoke GeneXpert MTB/RIF Ultra in Mozambique and Tanzania: a cost and cost-effectiveness analysis
- PMID: 40446169
- PMCID: PMC12124845
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0004724
Decentralized TB diagnostic testing with Truenat MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx vs. hub-and-spoke GeneXpert MTB/RIF Ultra in Mozambique and Tanzania: a cost and cost-effectiveness analysis
Abstract
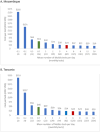
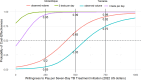
In low-and middle-income countries, missed or delayed tuberculosis (TB) diagnoses contribute to avoidable morbidity, mortality, and transmission. Decentralized testing platforms, such as the Molbio Truenat, may offer solutions by providing accurate point-of-care testing, improving access, and lowering out-of-pocket costs. Despite these advantages, the overall cost and cost-effectiveness of identifying additional TB cases using the Truenat MTB assays remain inadequately explored and understood. We collected economic data from a multicentre randomized controlled trial of TB testing using decentralized Molbio Truenat platform with MTB Plus and MTB-RIF Dx assays (Truenat MTB assays) versus hub-and-spoke Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra (standard of care) in Tanzania and Mozambique (TB-CAPT Core trial). We estimated facility-based diagnostic cost per participant tested and incremental facility-based diagnostic cost per incremental participant initiating TB treatment within seven and sixty days from enrolment. We used the societal perspective and conducted sensitivity analyses to determine key drivers of cost-effectiveness. The facility-based diagnostic cost per participant initiating treatment within seven days from enrolment in Mozambique was $853(95% uncertainty range: $707, $1072) for hub-and-spoke testing and $690($588, $823) for decentralized testing; in Tanzania costs were $596($485, $746) for hub-and-spoke testing and $592($495, $715) for decentralized testing. At sixty days, costs per treatment initiation were $581($493, $706) for hub-and-spoke vs. $678($576, $811) for decentralized testing in Mozambique, and $391($324, $476) vs. $591($494, $716) in Tanzania. Comparing decentralized to hub-and-spoke testing, the incremental cost per incremental seven-day treatment initiation was $403(-$103, $941) in Mozambique and $580($167, $1638) in Tanzania, and $805(-$10107, $10560) and -$353(-$20299, $20802) for sixty-day treatment initiation, respectively. Utilization (i.e., testing volume) of decentralized equipment was the strongest driver of cost-effectiveness. Decentralized TB testing with Truenat MTB assays is cost-effective relative to hub-and-spoke testing in Mozambique and Tanzania.
Copyright: © 2025 Malhotra et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Leukes VN, Hella J, Sabi I, Cossa M, Khosa C, Erkosar B, et al.. Study protocol: a pragmatic, cluster-randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effect of implementation of the Truenat platform/MTB assays at primary health care clinics in Mozambique and Tanzania (TB-CAPT CORE). BMC Infect Dis. 2024;24(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08876-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shah HD, Nazli Khatib M, Syed ZQ, Gaidhane AM, Yasobant S, Narkhede K, et al.. Gaps and Interventions across the Diagnostic Care Cascade of TB Patients at the Level of Patient, Community and Health System: A Qualitative Review of the Literature. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022;7(7):136. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed7070136 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Report of an Expert Consultation on the Uses of Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests for the Diagnosis of Tuberculosis. 2012. [cited 8 Jan 2024]. Available: https://www.cdc.gov/tb/publications/guidelines/amplification_tests/consi...
-
- World Health Organization. WHO operational handbook on tuberculosis. Module 3: diagnosis - rapid diagnostics for tuberculosis detention, 2021 update. 2021. Available: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/342369/9789240030589-eng.pdf...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
