Effect of complete, lifelong ANGPTL3 deficiency on triglyceride-rich lipoprotein kinetics
- PMID: 40446802
- PMCID: PMC12208341
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102152
Effect of complete, lifelong ANGPTL3 deficiency on triglyceride-rich lipoprotein kinetics
Abstract
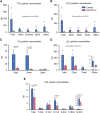
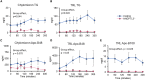
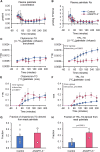
Angiopoietin-like 3 (ANGPTL3) inhibits lipases that hydrolyze triglycerides (TGs) in TG-rich lipoproteins (TRLs). We evaluated TRL-TGs, TRL particle (apolipoprotein B), palmitate, and glucose kinetics during a mixed-meal test that included intravenous and oral tracer administrations in people with extremely rare compound heterozygous ANGTPL3 loss-of-function mutations (ANGPTL3-/- group, n = 3) and matched control participants (n = 7). Multi-organ (liver, muscle, and adipose tissue) insulin sensitivity was evaluated with a two-step hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp procedure and glucose and palmitate tracer infusions. We find that plasma TG and TRL particle concentrations are more than 10-fold lower in the ANGPTL3-/- than in the control group due to both markedly reduced liver-derived TRL particle and TG secretion rates combined with increased plasma clearance of both liver- and gut-derived TRLs. Palmitate and glucose kinetics during the meal test are not different between the groups. We conclude that the biological function of ANGPTL3 reaches beyond inhibiting intravascular lipase activity.
Keywords: ANGPTL3; TG secretion; angiopoietin; hypolipidemia; lipoprotein kinetics; lipoprotein turnover; plasma TG clearance.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Converse C.A., Skinner E.R. Oxford University Press; 1992. Lipoprotein Analysis. - DOI
-
- Taskinen M.R., Matikainen N., Björnson E., Söderlund S., Inkeri J., Hakkarainen A., Parviainen H., Sihlbom C., Thorsell A., Andersson L., et al. Contribution of intestinal triglyceride-rich lipoproteins to residual atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in individuals with type 2 diabetes on statin therapy. Diabetologia. 2023;66:2307–2319. doi: 10.1007/s00125-023-06008-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

