A retrospective study on unfavorable 28-day neurological outcomes of stage II TB meningitis
- PMID: 40447639
- PMCID: PMC12125395
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-02708-2
A retrospective study on unfavorable 28-day neurological outcomes of stage II TB meningitis
Abstract
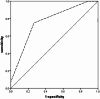
Tuberculous meningitis (TBM) is often associated with adverse neurological outcomes, however, there is a lack of relevant research. The aim of this study is to explore the risk factors that affect the poor prognosis of 28-day neurological function in patients with stage II TBM. A retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical data of patients with stage II TBM who visited our hospital from January 1st, 2018 to August 1st, 2019 based on the staging criteria of the Medical Research Council. The neurological function prognosis after 28 days of follow-up was determined to establish independent risk factors. A total of 138 patients (82 male and 56 female) were included, with an average onset age of 37.01 ± 17.30 years. Forty patients had poor prognosis (Modified Rankin Scale [MRS] score, 3-6 points), while 98 patients had a good prognosis (MRS score, 0-2 points). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that peripheral nerve dysfunction (odds ratio [OR], 6.315; 95% confidence interval [CI] 2.319-17.196; p < 0.001), Quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (QSOFA) score (OR 7.343; 95% CI 2.984-18.066; p < 0.001), and hydrocephalus (OR 2.685; 95% CI 1.020-7.068; p = 0.045) were independent risk factors. The area under the curve for predicting the 28-day neurological prognosis of patients with stage II TBM using the QSOFA score was 0.766 (95% CI 0.680-0.853; p < 0.001). Peripheral nerve dysfunction, QSOFA score, and hydrocephalus are independent risk factors for 28-day neurological dysfunction in patients with stage II TBM. The QSOFA score had good predictive ability of the prognosis in terms of 28-day neurological function of patients with stage II TBM.
Keywords: Disease staging; Prognosis; Risk factors; Tuberculous meningitis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of West China Hospital of Sichuan University (ethical code no. 2018 − 598). Due to the retrospective nature of the study, the Ethics Committee of West China Hospital of Sichuan University waived the need of obtaining informed consent’ in the manuscript. Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

