Targeting casein kinase 2 and ubiquitin-specific protease 7 to modulate RUNX2-mediated osteogenesis in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 40447997
- PMCID: PMC12125883
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-025-01222-5
Targeting casein kinase 2 and ubiquitin-specific protease 7 to modulate RUNX2-mediated osteogenesis in chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Objective: Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) frequently leads to Mineral Bone Disorder (MBD), which significantly affects patient quality of life due to bone fragility and metabolic disturbances. This study investigates the role of Casein Kinase 2 (CK2) and Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 7 (USP7) in modulating Runt-related Transcription Factor 2 (RUNX2)-driven osteogenesis in a CKD-MBD mouse model.
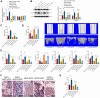
Methods: A CKD-MBD mouse model was established using 5/6 nephrectomy. Bioinformatic analysis of CKD-related datasets identified RUNX2 and USP7 as key genes implicated in bone metabolism. In vivo and in vitro experiments were conducted to assess the effects of CK2-mediated phosphorylation and USP7-induced deubiquitination on RUNX2 stability and function. Histomorphometry, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA), and micro-CT analyses were performed to evaluate bone density, strength, and metabolic markers.
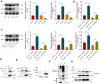
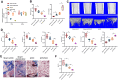
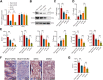
Results: RUNX2 and USP7 were significantly downregulated in CKD-MBD mice. Silencing RUNX2 impaired osteoblast differentiation, reduced bone density, and increased bone turnover, while CK2 overexpression restored RUNX2 activity by phosphorylation, recruiting USP7 to stabilize RUNX2. Enhanced osteoblast differentiation and improved bone metabolism were observed in CKD-MBD mice upon CK2 activation.
Conclusion: CK2 activation promotes RUNX2 phosphorylation and stabilization by USP7, leading to improved osteogenesis and bone metabolism in CKD-MBD. Targeting the CK2/USP7/RUNX2 axis presents a potential therapeutic strategy for managing CKD-related bone disorders.
Keywords: Casein kinase 2; Chronic kidney disease; Mineral bone metabolism disorder; Runt-related transcription factor 2; Ubiquitin-specific protease 7.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University under approval number 2021-311. The study does not involve clinical tissue experiments, and hence no clinical ethics approval was required. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

