TRPC6-targeted dexamethasone nanobubbles with ultrasound-guided theranostics for adriamycin-induced nephropathy
- PMID: 40448086
- PMCID: PMC12124086
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-025-03487-8
TRPC6-targeted dexamethasone nanobubbles with ultrasound-guided theranostics for adriamycin-induced nephropathy
Abstract
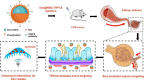
Background: Glucocorticoid (GC) intolerance and systemic toxicity pose significant challenges in the treatment of primary nephrotic syndrome (PNS), underscoring the urgent need for targeted therapies that maximize efficacy while minimizing adverse effects. To address these challenges, we developed TRPC6-targeted dexamethasone-loaded nanobubbles (Dex@NBs-TRPC6)-an innovative therapeutic platform that enables selective podocyte delivery alongside real-time monitoring capabilities.
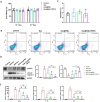
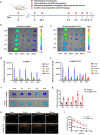
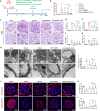
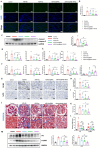
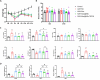
Results: The Dex@NBs-TRPC6 nanobubble system comprises polyethylene glycol-modified lipid vesicles encapsulating dexamethasone (Dex), conjugated with TRPC6-specific antibody for precise podocyte targeting delivery. Comprehensive in vivo and in vitro evaluations demonstrated the robust kidney and podocyte-targeting capabilities of Dex@NBs-TRPC6. Functional assays in mouse podocyte cells revealed that Dex@NBs-TRPC6 significantly outperformed free Dex and non-targeted nanobubbles (Dex@NBs) in mitigating cell apoptosis and inflammation. In an adriamycin-induced mouse nephropathy model, Dex@NBs-TRPC6, administered at half the dosage of free Dex, markedly alleviated proteinuria, glomerular and tubular damage, renal apoptosis, inflammation and fibrosis. Notably, Dex@NBs-TRPC6 attenuated the overexpression of hepatic gluconeogenic genes PCK1 and GCP6, a common adverse effect associated with Dex. Furthermore, leveraging the acoustic response properties of Dex@NBs-TRPC6, this delivery system integrates ultrasound imaging capabilities, enabling real-time visualization and therapeutic monitoring.
Conclusions: By simultaneously enhancing therapeutic efficacy, minimizing systemic toxicity, and enabling personalized imaging-guided treatment, Dex@NBs-TRPC6 introduces a transformative approach to GC-based renal therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments were in accordance with the National Institutes of Health guide for the care and use of Laboratory animals. All animal experiments were approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Nanjing Medical University (2206008). Consent for publication: All authors have provided consent for the manuscript to be published. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

