Longitudinal safety and efficacy of dual treatment with orthokeratology lenses and 0.01% atropine eye drops: a focus on epithelial changes and tear film stability
- PMID: 40448102
- PMCID: PMC12123784
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-025-04151-3
Longitudinal safety and efficacy of dual treatment with orthokeratology lenses and 0.01% atropine eye drops: a focus on epithelial changes and tear film stability
Abstract
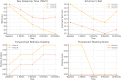
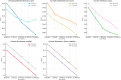
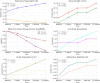
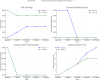
The longitudinal evaluation of the dual treatment protocol combining orthokeratology (Ortho-K) lenses and 0.01% atropine eye drops focused on assessing tear film stability, corneal epithelial alterations, and visual function in pediatric myopia control. This prospective, randomized study enrolled 100 participants aged 8 to - 18 years, categorized into Group A (Ortho-K + 0.01% atropine) and Group B (Ortho-K monotherapy). The subjects were followed for 12 months, with assessments at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months. The key parameters analyzed included axial length progression, spherical equivalent refraction, best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), corneal topography, corneal epithelial thickness, corneal endothelial cell density, intraocular pressure (IOP), tear break-up time (TBUT), Schirmer's test results, and ocular surface integrity determined via fluorescein and lissamine green staining. Compared with Group B (Δ0.5 ± 0.07 mm, p < 0.05), Group A exhibited superior myopia control, with a significant reduction in axial elongation (Δ0.3 ± 0.05 mm, p = 0.04). BCVA improved more in Group A (-0.1 ± 0.04 LogMAR, p = 0.03) than in Group B (-0.15 ± 0.04 LogMAR, p < 0.05). However, tear film stability decreased in Group A, as evidenced by a greater reduction in TBUT (Δ1.5 ± 0.3 s, p = 0.04) than in Group B (Δ0.7 ± 0.2 s, p = 0.05). Corneal epithelial thinning was more pronounced in Group A (Δ2.5 ± 0.5 μm, p = 0.05) than in Group B (Δ1.0 ± 0.3 μm, p = 0.07). No significant differences in Schirmer's test, endothelial cell density, or IOP were noted between the groups. Patient adherence was greater in Group A than in Group B (93% vs. 91%), and both groups reported high patient satisfaction scores. These findings suggested that dual therapy enhances myopia control while maintaining corneal and ocular surface integrity, although tear film stability and epithelial health require careful long-term monitoring. Further longitudinal studies with larger cohorts are necessary to confirm the long-term safety and efficacy of this combined approach.
Keywords: Atropine; Myopia control; Orthokeratology; Pediatric myopia; Tear film stability.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethic approval: The study received approval from the Ethics Committee of Foshan Fosun Chancheng Hospital(20215526). Consent to participate: We secured a signed informed consent form from every participant. Consent to publish: The manuscript has not been published before, and it is not being reviewed by any other journal. The authors have all approved the content of the paper. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Samir SA, Sharaf AF, Seht E, et al. Biometric data changes after penetrating corneal wounds in pediatric eyes. J Adv Med Med Res. 2023;35:69–76. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical