Nano-formulations in disease therapy: designs, advances, challenges, and future directions
- PMID: 40448105
- PMCID: PMC12123787
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-025-03442-7
Nano-formulations in disease therapy: designs, advances, challenges, and future directions
Abstract
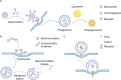
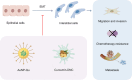
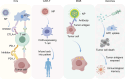
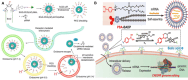
Nano-formulations, as an innovative drug delivery system, offer distinct advantages in enhancing drug administration methods, improving bioavailability, promoting biodegradability, and enabling targeted delivery. By exploiting the unique size advantages of nano-formulations, therapeutic agents, including drugs, genes, and proteins, can be precisely reorganized at the microscale level. This modification not only facilitates the precise release of these agents but also significantly enhances their efficacy while minimizing adverse effects, thereby creating novel opportunities for treatment of a wide range of diseases. In this review, we discuss recent advancements, challenges, and future perspectives in nano-formulations for therapeutic applications. For this aim, we firstly introduce the development, design, synthesis, and action mechanisms of nano-formulations. Then, we summarize their applications in disease diagnosis and treatment, especially in fields of oncology, pulmonology, cardiology, endocrinology, dermatology, and ophthalmology. Furthermore, we address the challenges associated with the medical applications of nanomaterials, and provide an outlook on future directions based on these considerations. This review offers a comprehensive examination of the current applications and potential significance of nano-formulations in disease diagnosis and treatment, thereby contributing to the advancement of modern medical therapies.
Keywords: Design strategies; Disease therapy; Hybrid nanoparticle; Nano-formulations.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects.J Nanobiotechnology. 2018 Sep 19;16(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12951-018-0392-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018. PMID: 30231877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nano-based drug delivery system for therapeutics: a comprehensive review.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2023 Aug 17;9(5). doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/acedb2. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2023. PMID: 37549657 Review.
-
Surface engineered multifunctional nano-systems for localised drug delivery against thyroid cancer: A review of current practices.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jul;176:116840. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116840. Epub 2024 May 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38820975 Review.
-
Advancements in nanomedicine: Precision delivery strategies for male pelvic malignancies - Spotlight on prostate and colorectal cancer.Exp Mol Pathol. 2024 Jun;137:104904. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2024.104904. Epub 2024 May 25. Exp Mol Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38788248 Review.
-
Nanotechnology-empowered combination therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: principles, strategies, and challenges.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jul 22;22(1):431. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02670-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39034407 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial Intelligence-Driven Strategies for Targeted Delivery and Enhanced Stability of RNA-Based Lipid Nanoparticle Cancer Vaccines.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 30;17(8):992. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17080992. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40871015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nano-Phytomedicine: Harnessing Plant-Derived Phytochemicals in Nanocarriers for Targeted Human Health Applications.Molecules. 2025 Jul 29;30(15):3177. doi: 10.3390/molecules30153177. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40807355 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jeevanandam J, Chan YS, Danquah MK. Nano-formulations of drugs: recent developments, impact and challenges. Biochimie. 2016;128–129:99–112. - PubMed
-
- Soppimath KS, Aminabhavi TM, Kulkarni AR, et al. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J Control Release. 2001;70(1–2):1–20. - PubMed
-
- Erdoğar N, Akkın S, Bilensoy E. Nanocapsules for drug delivery: an updated review of the last decade. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2018;12(4):252–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

