Combined Distal Femoral Osteotomy and Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction for Patellar Instability and Genu Valgus: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 40448506
- PMCID: PMC12214406
- DOI: 10.1111/os.70057
Combined Distal Femoral Osteotomy and Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction for Patellar Instability and Genu Valgus: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
Background: Medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) reconstruction alone is not effective for patellar instability associated with anatomic abnormalities of lower limbs. In this article, we report a case of complex lower limb malformations, including genu valgus, lower limb shortening, and increased femoral anteversion angle. In addition to MPFL reconstruction, we performed a rare osteotomy named combined distal femoral osteotomy (CDFO), which combined the characteristics of lateral opening wedge distal femoral osteotomy (LOWDFO) and derotational distal femoral osteotomy (DDFO).
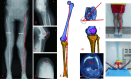
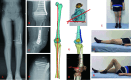
Case presentation: We report the case of a 52-year-old female with left knee pain, valgus, and instability who was diagnosed with patellar instability and valgus knee osteoarthritis. Considering the patient's relatively young age, a hip-knee-ankle angle (HKA) of 194°, a mechanical lateral distal femoral angle (mLDFA) of 77.5°, a shortened left lower limb of 7 mm, an increased femoral anteversion angle (FAA) of 37.4°, and a patellar instability, we performed MPFL reconstruction and CDFO treatment. In this procedure, computer-aided design (CAD) combined 3D-printed osteotomy guide-assisted CDFO and MPFL reconstruction were performed. At 6-month follow-up, the patient achieved satisfactory results, with an HKA of 180°, an mLDFA of 90°, an FAA of 15°, the same length of lower limbs, and patellar stability. There was significant improvement in her left knee pain, function, and patellar stability.
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this rare pattern of patellar instability has not been previously described. Careful analysis of anatomic abnormalities is of great clinical significance and can better guide clinical treatment. CDFO may be an acceptable treatment for patellar instability with genu valgus and increased femoral anteversion angle.
Keywords: derotational distal femoral osteotomy; genu valgus; lateral opening wedge distal femoral osteotomy; medial patellofemoral ligament; patellar instability.
© 2025 The Author(s). Orthopaedic Surgery published by Tianjin Hospital and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Derotational distal femoral osteotomy improves subjective function and patellar tracking after medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction in recurrent patellar dislocation patients with increased femoral anteversion: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2024 Jan;32(1):151-166. doi: 10.1002/ksa.12021. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2024. PMID: 38226710
-
Concomitant distal femoral osteotomy in managing chronic patellofemoral instability with an associated valgus deformity: A case report and review of literature.J ISAKOS. 2025 Jun;12:100860. doi: 10.1016/j.jisako.2025.100860. Epub 2025 Apr 8. J ISAKOS. 2025. PMID: 40210165 Review.
-
Distal femoral osteotomies improves recurrent patellar instability in patients with genu valgum: A systematic review.J ISAKOS. 2024 Dec;9(6):100318. doi: 10.1016/j.jisako.2024.100318. Epub 2024 Sep 10. J ISAKOS. 2024. PMID: 39260775
-
Lateral Opening Distal Femoral Osteotomy With Concomitant Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Is Efficacious in Addressing Patellar Instability.Arthroscopy. 2025 Aug;41(8):2927-2937. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2024.12.016. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Arthroscopy. 2025. PMID: 39710155
-
Varus Producing Distal Femur Osteotomy Alters Radiographic Measurements Related to Patellofemoral Instability: A Cadaver Study.J Knee Surg. 2025 Jul;38(9):463-468. doi: 10.1055/a-2542-2639. Epub 2025 Feb 20. J Knee Surg. 2025. PMID: 39978397
References
-
- Danielsen O., Poulsen T. A., Eysturoy N. H., Mortensen E. S., Hölmich P., and Barfod K. W., “Trochlea Dysplasia, Increased TT‐TG Distance and Patella Alta Are Risk Factors for Developing First‐Time and Recurrent Patella Dislocation: A Systematic Review,” Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy 31, no. 9 (2023): 3806–3846, 10.1007/s00167-022-07255-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

