P-glycoprotein modulates the fluidity gradient of the plasma membrane of multidrug resistant CHO cells
- PMID: 40448544
- PMCID: PMC12338861
- DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.70083
P-glycoprotein modulates the fluidity gradient of the plasma membrane of multidrug resistant CHO cells
Abstract
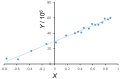
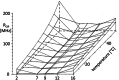
Cryo-electron microscopy has yielded high-resolution structural data of the multidrug efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (ABCB1), but its direct and indirect interactions within the native membrane environment have remained largely unexplored. Here, we compared the fluidity gradients of plasma membranes of the drug-sensitive CHO cell line AuxB1 and its P-glycoprotein overexpressing derivative B30 by fluorescence anisotropy of embedded n-(9-anthroyloxy) fatty acid probes (n = 2, 7, 9, 12, 16) in the temperature range of 10-50 °C. The shape of the temperature profiles of probe mobility was comparable in AuxB1 and B30 membranes, but did not match. Overexpression of P-glycoprotein smoothened the transversal gradient of the out-of-plane mode of rotation of the probes, which may facilitate the partitioning of hydrophobic drugs into the membrane and thereby increase the speed of P-glycoprotein to pump the drug out of the cell.
Keywords: ABC transporter; ABCB1; P‐glycoprotein; membrane fluidity; multidrug resistance; n‐(9‐anthroyloxy) fatty acid.
© 2025 The Author(s). FEBS Letters published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Riordan JR and Ling V (1979) Purification of P‐glycoprotein from plasma membrane vesicles of Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants with reduced colchicine permeability. J Biol Chem 254, 12701–12705. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

