Dietary resveratrol alleviates liver and intestinal injury in ducks under cage rearing system
- PMID: 40449104
- PMCID: PMC12166879
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105330
Dietary resveratrol alleviates liver and intestinal injury in ducks under cage rearing system
Abstract
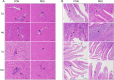
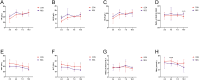
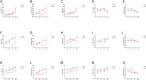
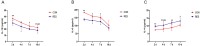
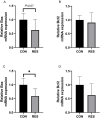
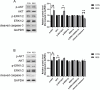
Cage rearing is a promising farming method. However, our previous studies have demonstrated that changes in farming practices induce oxidative stress and inflammation in the liver and duodenum of ducks. Resveratrol (RES), a natural plant polyphenol, possesses antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cytoprotective properties. This study evaluated the alleviating effects of RES against cage-rearing-induced duck health problems, emphasizing the involvement of redox imbalance, inflammatory response, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, apoptosis, and PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways. A total of 120 healthy 12-week-old female ducks were transferred to a cage system and randomly assigned to two dietary RES groups with 6 replicates each (10 ducks per replicate), including basal diet + 0 mg/kg RES (control group, CON), and basal diet + 500 mg/kg RES (RES-treated group, RES). During the early stages (within 10 days) of cage rearing, blood, liver, and duodenal samples were collected for analysis. The results demonstrated that RES reduced histopathological damage in the liver and duodenum of cage-reared ducks. It also reduced serum albumin levels, increased serum aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase levels, and enhanced antioxidant (increased CAT, GSH-Px, SOD, and T-AOC activities in the serum, liver, and duodenum, and reduced the increase in MDA) and anti-inflammatory properties (reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6 secretion and increased anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-4 levels). Additionally, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction revealed that RES intervention reversed the abnormal mRNA abundance of biomarkers associated with inflammatory injury (iNOS and COX2) in the liver, and ER stress (GRP78) and apoptosis (Bax and Bcl2) in the liver and duodenum of cage-reared ducks. Further analysis of key proteins in the PI3K/AKT and ERK MAPK signaling pathways revealed that RES promoted AKT phosphorylation in the liver and duodenum of cage-reared ducks and reduced cleaved caspase-3 protein content. Overall, RES prevents cage-rearing stimuli-induced liver and intestinal injury in ducks by enhancing liver function, improving antioxidant properties, inhibiting inflammation, ER stress, and apoptosis, and activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Keywords: Cage rearing; Duck; Inflammation; Oxidative stress; Resveratrol.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
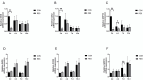
Similar articles
-
Palygorskite improves growth performance and prevents liver damage in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli-challenged broiler chickens at an early age.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae302. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae302. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39373204
-
Effects of 3-indoleacrylic acid on alleviating lipopolysaccharide-induced liver inflammatory damage in laying hens.Poult Sci. 2025 Aug;104(8):105307. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105307. Epub 2025 May 16. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40446688 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary resveratrol supplementation alleviates cold exposure-induced pyroptosis and inflammation in broiler heart by modulating oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress.Poult Sci. 2024 Nov;103(11):104203. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104203. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39178816 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of p53 regulation of oxidative stress in skeletal muscle.Redox Rep. 2018 Dec;23(1):100-117. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2017.1416773. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Redox Rep. 2018. PMID: 29298131 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory potential of dietary soybean-derived saponins.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae349. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae349. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39529449 Review.
References
-
- Bellizzi Y., Anselmi Relats J.M., Cornier P.G., Delpiccolo C.M.L., Mata E.G., Cayrol F., Cremaschi G.A., Blank V.C., Roguin L.P. Contribution of endoplasmic reticulum stress, MAPK and PI3K/akt pathways to the apoptotic death induced by a penicillin derivative in melanoma cells. Apoptosis. 2022;27:34–48. doi: 10.1007/s10495-021-01697-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Burguete M.C., Jover-Mengual T., Castelló-Ruiz M., López-Morales M.A., Centeno J.M., Aliena-Valero A., Alborch E., Torregrosa G., Salom J.B. Cerebroprotective effect of 17β-estradiol replacement therapy in ovariectomy-induced post-menopausal rats subjected to ischemic stroke: role of MAPK/ERK1/2 pathway and PI3K-independent akt activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023;24 doi: 10.3390/ijms241814303. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

