MFAP4 Deficiency Attenuates Liver Fibrosis by Regulating Hepatic Stellate Cell Fate Through Inhibition of the FAK/PI3K/NFκB Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 40449846
- PMCID: PMC12355556
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2025.101548
MFAP4 Deficiency Attenuates Liver Fibrosis by Regulating Hepatic Stellate Cell Fate Through Inhibition of the FAK/PI3K/NFκB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Background & aims: Liver fibrosis, driven by chronic injury, hinges on hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) activation. Microfibrillar-associated protein 4 (MFAP4), an extracellular matrix protein critical for elastic fiber assembly, is up-regulated in hepatic fibrosis, yet its mechanistic role remains unclear.
Methods: Liver fibrosis was induced in wild-type and Mfpa4 knockout mice using CCl4 and TAA, whereas LX-2 cells were activated with transforming growth factor-β1. Bioinformatics analysis, histopathology, double immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, Transwell coculture systems, Western blot, and quantitative polymerase chain reaction were used to identify the primary intrahepatic cell types expressing MFAP4 and assess its effects on HSCs activation and apoptosis.
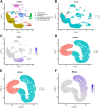
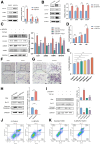
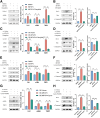
Results: MFAP4 is up-regulated in cirrhotic livers and is actively expressed in HSCs. Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis and Transwell coculture experiments revealed that the profibrotic effects of MFAP4 were primarily mediated through HSCs rather than hepatocytes. Inhibition of MFAP4 significantly reduces the expression of fibrosis markers in HSCs, inhibits their proliferation and migration, whereas overexpression of MFAP4 results in the opposite effect, accompanied by enhanced apoptosis resistance. In mouse models, global knockout of Mfap4 significantly alleviates CCl4- and TAA-induced liver fibrosis. Mechanistic analysis reveals that MFAP4 binds to integrin αvβ3 on the HSCs membrane, activating the FAK/PI3K/NFκB signaling pathway, which promotes HSC activation and survival, ultimately exacerbating liver fibrosis. Moreover, MFAP4 mediates a self-sustaining feedback loop via integrin αvβ3, maintaining HSCs activation and further promoting fibrosis progression.
Conclusions: MFAP4 governs HSCs activation and apoptosis resistance via integrin αvβ3-dependent FAK/PI3K/NFκB signaling. Targeting MFAP4 mitigates fibrosis by altering HSCs fate.
Keywords: Cell Fate; Hepatic Stellate Cell; Integrin; Liver Fibrosis; MFAP4.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures











References
-
- Kisseleva T., Brenner D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18:151–166. - PubMed
-
- Meng D., Li Z., Wang G., et al. Carvedilol attenuates liver fibrosis by suppressing autophagy and promoting apoptosis in hepatic stellate cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:1617–1627. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

