Preserving fruit freshness with amyloid-like protein coatings
- PMID: 40450027
- PMCID: PMC12126486
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60382-4
Preserving fruit freshness with amyloid-like protein coatings
Abstract
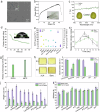
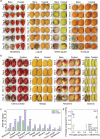
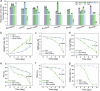
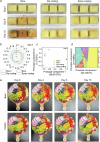
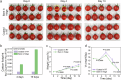
Addressing critical challenges in perishable fruit preservation, including hydrophobic surface treatment, protective layer adhesion on complex cuticles, and synergistic integration of preservation components, here we present an eco-friendly amyloid-like protein coating strategy developed through computer-aided molecular simulation. This system employs phase-transitioned lysozyme as an adhesive layer bonded to fruit epicuticular wax, synergized with sodium alginate and cellulose nanocrystals to form a proteinaceous barrier. Validated across 17 fruit varieties, the coating extends shelf-life by 2-5-fold through microbial inhibition, moisture loss reduction, and rot delay, while maintaining 60-98% nutrient retention, surpassing chemical preservation efficacy without toxicity risks. With edible properties, easy washability, and low cost, the coating demonstrates universal applicability for post-harvest and fresh-cut fruits. Notably, it reduces carbon dioxide emissions by 90% versus refrigeration while achieving 2.5-fold longer shelf-life. These positions the amyloid-like protein coating as a practical and sustainable approach to mitigating global food waste issues.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- FAO, IFAD, UNICEF, WFP and WHO. The state of food security and nutrition in the world 2020: Transforming food systems for affordable healthy diets. (2020).
-
- Springmann, M. et al. Options for keeping the food system within environmental limits. Nature562, 519–525 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Wu, W. et al. Structures and functions of cuticular wax in postharvest fruit and its regulation: a comprehensive review with future perspectives. Engineering23, 118–129 (2023).
-
- Asrey, R. et al. Genetically modified fruit and vegetable-An overview on senescence regulation, postharvest nutraceutical quality preservation and shelf life extension. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotech.96, 271–287 (2021).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

