Sasanlimab plus BCG in BCG-naive, high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: the randomized phase 3 CREST trial
- PMID: 40450141
- PMCID: PMC12353837
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-025-03738-z
Sasanlimab plus BCG in BCG-naive, high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: the randomized phase 3 CREST trial
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Sasanlimab plus BCG in BCG-naive, high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: the randomized phase 3 CREST trial.Nat Med. 2025 Aug;31(8):2815. doi: 10.1038/s41591-025-03894-2. Nat Med. 2025. PMID: 40691368 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
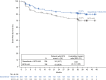
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) induction and maintenance (I+M) after transurethral resection of bladder tumor is standard of care (SOC) in high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC). However, disease recurrence/progression occurs in approximately 40% of patients at 2 years, with unfavorable prognosis. Limited bladder-sparing therapeutic options exist, and no improvements to response durability have been observed in decades. CREST is a global, phase 3, randomized trial evaluating subcutaneous sasanlimab in combination with BCG-I+M (Arm A), sasanlimab in combination with BCG-I (Arm B) or BCG-I+M (Arm C) in BCG-naive high-risk NMIBC. The primary endpoint was investigator-assessed event-free survival (EFS) for Arm A versus Arm C; key secondary endpoints were EFS (Arm B versus Arm C) and overall survival. Patients were randomized 1:1:1 to Arm A (N = 352), Arm B (N = 352) and Arm C (N = 351). The trial met its primary endpoint with a statistically significant and clinically meaningful prolongation of EFS (Arm A versus Arm C); hazard ratio, 0.68 (95% confidence interval: 0.49-0.94); one-sided P = 0.0095. The 36-month estimated EFS rates were 82.1% (Arm A) and 74.8% (Arm C). EFS benefit for Arm A versus Arm C was observed across prespecified subgroups, including carcinoma in situ (CIS) and T1. The safety profile of the combination was consistent with the known profiles. To our knowledge, sasanlimab is the first anti-PD-1 antibody to show a clinically meaningful prolongation of EFS when combined with BCG-I+M versus SOC in patients with BCG-naive high-risk NMIBC. Sasanlimab combined with BCG-I+M has the potential to redefine the treatment paradigm and clinical decision-making for patients with BCG-naive high-risk NMIBC. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04165317 .
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: N.D.S. reports research/consulting: Allessa, Amgen, Artera, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Aura Biosciences, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Caris, CG Oncology, Daiichi Sankyo, Dendreon, Glytheryx, Invitae, Janssen, MDxhealth, Merck, Minomic, Novartis, Nusano, PhotoCure, Pfizer, Sumitomo, Telix, Tolmar, Tutelix and Urogen. T.B.P. reports honoraria: Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Elexis, Gilead, Incyte, Ipsen, Johnson & Johnson, Mashup, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merck Serono, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and Seagen; consulting or advisory role: Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Elexis, Gilead, Incyte, Ipsen, Johnson & Johnson, Mashup, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merck Serono, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and Seagen; research funding: Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Elexis, Incyte, Ipsen, Johnson & Johnson, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merck Serono, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and Seagen; and travel, accommodations or expenses: Astellas, AstraZeneca, Gilead, Ipsen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer and Roche. J. Bedke reports financial interests from Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Ipsen, Janssen, Merck Sorono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, Roche, Nektar, Novartis and Seagen and membership in the European Association of Urology and the Renal Cell Carcinoma Guidelines Panel (Vice-Chairman). M.D.G. reports stock and other ownership interests: Pfizer, Merck and Gilead Sciences; research funding: Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, Mirati Therapeutics, Seagen, Alliance Foundation Trials, Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology, Clovis Oncology, Arvinas, ALX Oncology, Hoosier Cancer Research Network, Novartis, Acrivon Therapeutics, Astellas, Genentech, Accuray, PCCTC, G1 Therapeutics, OncoC4, Flare Therapeutics, Loxo/Lilly, Roche and Pfizer; other relationships: Elsevier, Medscape and Research to Practice; uncompensated relationships: G1 Therapeutics and Loxo/Lilly. J.P.R. reports advisory/consultancy roles for Arquer Diagnostics, Biotech, BTA Pharmaceuticals, Combat, Genomic Expression and Olympus; steering committee membership for AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen and Pfizer; grant or research support from Arquer Diagnostics, Biotech, BTA Pharmaceuticals, Cepheid, TARIS Biomedical and Nucleix; and research funding from Pfizer. J.H.K. reports research funding from Pfizer. M.K. reports research funding from Pfizer. E.X. reports consulting or advisory role: Pfizer, Ferring and Boston Scientific and research funding: Ferring and Pfizer. B.A. reports honoraria: AstraZeneca, Astellas, Eisai, Janssen, Bayer, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merck, Pfizer, Roche and Bristol Myers Squibb; consulting or advisory role: AstraZeneca, Astellas, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Merck, Pfizer, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Roche and Eisai; speakers’ bureau: Janssen, Astellas, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Eisai and Roche; research funding: AstraZeneca, Merck, Bayer, Astellas, Janssen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, ICON Clinical Research, Eisai, Merck Sharp & Dohme and Roche; and travel, accommodations and expenses: AstraZeneca, Astellas, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer and Sanofi. D.Y. reports research funding from Pfizer. F.G.-R. reports research support/principal investigator: Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, Taris, Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche, Seagen, AstraZeneca, Combat Medical, Cepheid, Fidia, Astellas, UroGen and Merck Sharp & Dohme; employment: SERMAS (Servicio Madrileño de Salud); consultancy: Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, Merck, Roche, Taris, Combat Medical, AstraZeneca, Merck Sharp & Dohme and Bristol Myers Squibb; stockholder: CG Oncology; speakers’ bureau: Janssen, Nucleix, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Palex, Combat Medical, Johnson & Johnson and Recordati; travel: Pfizer, Recordati, Ipsen, Combat Medical, Alter, Salvat, Nucleix, AstraZeneca, Fidia and Johnson & Johnson; advisory board: AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Combat Medical, Johnson & Johnson, Nucleix, Pfizer, Taris, Roche and Merck Sharp & Dohme; and manuscript support: Pfizer, Janssen, Combat Medical, AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson and Bristol Myers Squibb. A.B. reports consulting or advisory role: Astellas, Janssen-Cilag, OPKO Health, MDxHealth, Ferring, Bayer, AstraZeneca, Hauora and Pfizer; speakers’ bureau: Astellas; and research funding: Sandoz-Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme and Pfizer. G.S.K. reports honoraria: AbbVie, Tersera, Bayer, Knight Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca Canada and PhotoCure; consulting or advisory role: Merck, Theralase, Janssen Oncology, Ferring, Verity Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Myers Squibb, EMD Serono, Pfizer, Novartis and enGene; research funding: Johnson & Johnson/Janssen and Pfizer. J. Brinkmann reports employment: Pfizer Pharma GmbH. A.-M.C. reports employment: Pfizer SRL. R.C. reports employment: Pfizer SRL. A.E. reports employment: Pfizer Ltd. E.M. reports employment: Pfizer Inc. J.V. reports employment: Pfizer Inc. C.W. reports employment: Pfizer Inc. G.D.S. reports advisory/consultancy roles: Heat Biologics, CG Oncology, PhotoCure, Merck, Roche/Genentech, Ciclomed, Taris Biomedical (now Janssen), MDxHealth, Fidia Farmaceutici, UroGen, Ferring, Aduro, Boston Scientific, Bristol Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Janssen, Epivax Therapeutics, Natera, FKD, EnGene Bio, Sesen Bio, BioCanCell (now Archiano), Nucleix, Ipsen, Combat Medical, Astellas, FerGene, Dendreon, AbbVie, Seagen, Verity Pharmaceuticals, Regeneron, STIMIT, Vyriad, Protara, xCures, Nonagen, Nanology and Imvax; clinical trial protocol committee membership for Bristol Myers Squibb, CG Oncology, Fidia, Janssen, Merck, Pfizer, PhotoCure, Protara and Seagen; stock/shares in CG Oncology, EnGene Bio, EpiVax Therapeutics and UroGen; and research funding from Pfizer.
Figures








References
-
- Bray, F. et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin.74, 229–263 (2024). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

