Carbon nanotubes/ordered mesoporous carbon/chitosan nanocomposite as a promising carrier for everolimus targeted delivery toward lung cancer cells
- PMID: 40450161
- PMCID: PMC12126314
- DOI: 10.1007/s10856-025-06901-7
Carbon nanotubes/ordered mesoporous carbon/chitosan nanocomposite as a promising carrier for everolimus targeted delivery toward lung cancer cells
Abstract
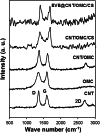
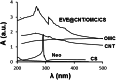
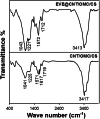
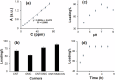
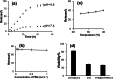
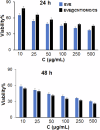
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide. Everolimus (Eve) was observed to upregulate the expression of phosphatase and tensin homolog and microRNA-4328 and inhibits the proliferation and migration of A549 cells. In the present study, a new nanocarrier based on composite containing chitosan (CS), carbon nanotubes (CNT) and ordered mesoporous (OMC) was used to load the anticancer drug everolimus (EVE). The existence of EVE on CNT/OMC/CS nanocarrier is confirmed by FE-SEM images, Raman, UV-Vis, FT-IR, BET and TGA analyses. The results showed that the introduction of CS improved the drug loading by 89.4% at pH 7.0, time 2 h and EVE to CNT/OMC/CS ratio of 1.5. Moreover, release study of EVE showed that 15.2% of EVE is released from EVE@CNT/OMC/CS at pH=7.4 for 15 h, while 78.9% of EVE is released at pH = 4.5. After 25 h, 16.8% and 88.0% of EVE were released at pH 7.4 and 4.5, respectively. Based on the MTT assay results, CNT/OMC/CS exhibited negligible cytotoxicity and good compatibility on the A549 lung cancer cell line. The cytotoxicity of the EVE@CNT/OMC/CS (IC50 of ~9 μg/mL) on the A549 cell line was higher as compared to free Eve drug (IC50 of ~13 μg/mL) after 48 h exposure time. All the data confirmed the synergistic effect of EVE in combination with CNT/OMC/CS could serve as an ideal candidate in treating lung cancer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declares no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Taghavi S, Abnous KH, Taghdisi SM, Ramezani M, Alibolandi M. Hybrid carbon-based materials for gene delivery in cancer therapy. J Control Rel. 2020;318:158–75. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

