Investigating the effect of breastfeeding counselling based on latch, position and Information-Motivation-Behavior model on maternal and neonatal indices: a clinical trial
- PMID: 40450206
- PMCID: PMC12126870
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-025-07679-w
Investigating the effect of breastfeeding counselling based on latch, position and Information-Motivation-Behavior model on maternal and neonatal indices: a clinical trial
Abstract
Background and objectives: This study compares the impact of breastfeeding counselling based on the Information-Motivation-Behavior model (IMB) with routine counselling at the breastfeeding counselling center on certain health indices of mothers and their infants.
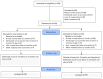
Methods: The present study is a clinical trial using a convenient sampling method conducted randomly on the referred mothers and their infants. Participants were allocated into two groups "routine counseling at the breastfeeding counseling center" and "breastfeeding counseling based on the Information-Motivation-Behavior Model" (59 mothers and their infants in each group). Demographic information, WHO breastfeeding observation form, latch assessment form, infant weight, maternal body mass index (BMI), blood pressure, and postpartum depression questionnaire were filled. Outcomes were reassessed at 2, 4, and 6 months of children's age for both groups. The infant behaviour questionnaire was completed only at 6 months.
Results: The two groups were similar in terms of demographic variables and obstetric history, such as maternal education (p = 0.589), spouse's occupation (p = 0.457), wanted/unwanted pregnancy (p = 0.154), and delivery type (p = 0.349). In the intervention group, significant differences were found compared to the routine counseling group in postpartum depression scores (p-value = 0.030), body mass index (p-value < 0.001), latch assessment scores (p-value < 0.001), and total WHO breastfeeding observation form scores (p-value < 0.001). In this study, the results were in favor of the intervention group. These differences became observable from the second month, leading to the continuation of exclusive breastfeeding and a reduction in maternal dropout rates.
Conclusion: Application of counselling with the IMB model can motivate correct breastfeeding behaviours and improve maternal and infant health indices.
Trial registration: This trial is registered with the Iranian Registry of Clinical Trial with the identifier IRCT20170611034452N15 (registration date 20230428).
Keywords: Breastfeeding counseling; IMB model; Maternal and infant health indices.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Ethics approval was obtained (IR.KMU.REC.1402/012) from the Ethics Committee of Kerman University of Medical Sciences. Participants were assured of confidentiality and anonymity. The study protocol was registered in the Iranian Clinical Trial Registry (IRCT20170611034452N15/(registration date: 2023-04-28)). Human Ethics and Consent to Participate declarations: All of the intervention process was in line with the Helsinki declaration. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Support for healthy breastfeeding mothers with healthy term babies.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Oct 25;10(10):CD001141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001141.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36282618 Free PMC article.
-
Breastfeeding education and support for women with twins or higher order multiples.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 28;2(2):CD012003. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012003.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28244065 Free PMC article.
-
Antenatal breastfeeding education for increasing breastfeeding duration.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Dec 6;12(12):CD006425. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006425.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27922724 Free PMC article.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 6;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21735394
-
Psychosocial interventions for supporting women to stop smoking in pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 14;2(2):CD001055. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001055.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28196405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rapheal SM, et al. LATCH score for identification and correction of breastfeeding problems—a prospective observational study. Indian Pediatr. 2023;60(1):37–40. - PubMed
-
- Bourdillon K, McCausland T, Jones S. Latch-related nipple pain in breastfeeding women: the impact on breastfeeding outcomes. Br J Midwifery. 2020;28(7):406–14.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical