Association of Life's Crucial 9 with cognitive function and stroke risk: insights from the NHANES 2011-2014 study
- PMID: 40450265
- PMCID: PMC12125833
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-025-23259-1
Association of Life's Crucial 9 with cognitive function and stroke risk: insights from the NHANES 2011-2014 study
Abstract
Background: Cognitive impairment and stroke constitute major health challenges for the aging global population, adversely impacting quality of life and increasing healthcare burdens. The American Heart Association's "Life's Essential 8" (LE8) framework has served as a key tool for evaluating cardiovascular health (CVH); however, it omits mental health, a critical factor influencing both cognitive function and stroke risk. The introduction of "Life's Crucial 9" (LC9), which includes depressive symptoms, provides a more comprehensive approach. This study investigates the relationship between LC9, cognitive function, and stroke risk.
Methods: Utilizing the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) dataset from 2011 to 2014, cross-sectional data from 2,327 participants were analyzed. Stratified analyses were performed according to demographic and health-related factors. A Restricted Cubic Spline (RCS) model was employed to examine potential threshold effects. Additionally, weighted linear regression models were used to evaluate cognitive performance, and logistic regression models were applied to assess stroke risk.
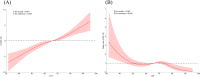
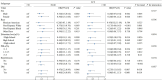
Results: Higher LC9 scores were positively associated with better cognitive function and lower odds of stroke. Within the cognitive function analysis, higher LC9 scores were significantly associated with superior performance on the Digit Symbol Substitution Test (DSST) (β = 0.18, 95% CI: 0.11- 0.26, P < 0.001). In the stroke analysis, individuals with higher LC9 scores exhibited decreased odds of experiencing a stroke (OR = 0.97, 95% CI: 0.95-0.99, P = 0.005). RCS analysis identified a non-linear relationship between LC9 scores and the odds of stroke, with the greatest decreases in stroke odds observed at lower LC9 scores, plateauing around a score of 70.
Conclusions: Higher LC9 scores are associated with better cognitive function and lower odds of stroke. These findings suggest that incorporating mental health metrics, such as depression, into cardiovascular health assessments enhances the predictive power for cognitive outcomes and stroke prevention.
Keywords: Cognitive function; LC9; NHANES; Stroke.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Data collection for the NHANES was approved by the NCHS Research Ethics Review Board (ERB). An individual investigator utilizing the publicly available NHANES data do not need to file the institution internal review board (IRB). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Life's crucial 9 is inversely and linearly associated with female infertility prevalence: a cross-sectional analysis from NHANES 2013-2018.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 28;15(1):14918. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99023-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40295619 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Life's Crucial 9 with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in stroke survivors and predictive value for mortality compared with Life's Essential 8: evidence from NHANES 2005-2018.Front Neurol. 2025 Mar 17;16:1519954. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1519954. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40166635 Free PMC article.
-
Association between life's essential 8 and cognitive impairment in older patients: results from NHANES 2011-2014.BMC Geriatr. 2024 Nov 14;24(1):943. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05547-4. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 39543520 Free PMC article.
-
The association between life's crucial 9 and all-cause, cancer-specific and cardiovascular mortality in US cancer survivors: a cohort study of NHANES.BMC Cancer. 2025 Apr 30;25(1):805. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14229-2. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40307773 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-response associations of the American Heart Association's new "Life's essential 8" metrics with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in a nationally representative sample from the United States.Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2024 Jul-Aug;85:31-37. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2024.06.001. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 38925257 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between life's crucial 9 and major eye diseases among US adults aged 40 years or older.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jul 19;25(1):2504. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-23704-1. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40684142 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Nieuwkerk AC, et al. Cognitive impairment in patients with cardiac disease: implications for clinical practice. Stroke. 2023;54:2181–91. 10.1161/strokeaha.123.040499. - PubMed
-
- 2022 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s & dementia: the journal of the Alzheimer’s Association 18, 700–789. 10.1002/alz.12638 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Orgeta V, Mukadam N, Sommerlad A, Livingston G. The lancet commission on dementia prevention, intervention, and care: a call for action. Ir J Psychol Med. 2019;36:85–8. 10.1017/ipm.2018.4. - PubMed
-
- Ovbiagele B, et al. Forecasting the future of stroke in the united States: a policy statement from the American heart association and American stroke association. Stroke. 2013;44:2361–75. 10.1161/STR.0b013e31829734f2. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

