Evaluating the precision and reproducibility of cephalometric landmarks in locally reconstructed lateral cephalometric radiographs from cone beam computed tomography (CBCT)
- PMID: 40450295
- PMCID: PMC12125902
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-025-06258-x
Evaluating the precision and reproducibility of cephalometric landmarks in locally reconstructed lateral cephalometric radiographs from cone beam computed tomography (CBCT)
Abstract
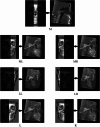
Objective: The commonly used lateral cephalometric radiographs, including traditional lateral cephalometric radiographs and CBCT-synthesized lateral cephalometric radiographs, have the problem of overlapping anatomical structures, which interferes with the identification of landmarks. Therefore, we proposed a new method called CBCT-based locally reconstructed lateral cephalometric radiographs and evaluated its precision and reproducibility.
Materials and methods: CBCT and lateral cephalometric radiographs were obtained from five orthodontic patients. Twenty-six cephalometric landmarks were identified using three methods by ten orthodontists. The landmarks on each image were recorded as (X, Y), and the absolute values of the differences between each measurement and the average values of the X and Y coordinates were calculated (ΔX and ΔY). Additionally, the distance between each located point and the centroid was calculated (ΔD). The differences in ΔX, ΔY, and ΔD among the groups were compared through analysis of variance (ANOVA). Bonferroni post hoc correction was used for pairwise comparisons. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
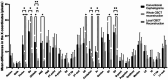
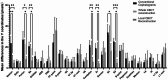
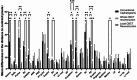
Results: The reproducibility of 14 landmarks in the CBCT-based locally reconstructed lateral cephalometric radiographs was better than that of the other methods in at least one direction (p < 0.05). Among these landmarks, the precision of the CBCT local reconstruction group was greater in all directions for five landmarks than that of the other two groups (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The CBCT locally reconstructed lateral cephalometric radiographs proposed in this study enhanced the precision and reproducibility of cephalometric landmark identification.
Keywords: Cephalometric analysis; Cephalometric landmarks; Cone beam computed tomography; Precision and reproducibility.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the ethics committee of the Chinese PLA General Hospital (No. 2024165). Written informed consent to participate was obtained from the participants. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reliability of anatomic structures as landmarks in three-dimensional cephalometric analysis using CBCT.Angle Orthod. 2014 Sep;84(5):762-72. doi: 10.2319/090413-652.1. Epub 2013 Dec 23. Angle Orthod. 2014. PMID: 24364751 Free PMC article.
-
Precision of cephalometric landmark identification: cone-beam computed tomography vs conventional cephalometric views.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009 Sep;136(3):312.e1-10; discussion 312-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2008.12.018. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009. PMID: 19732656 Free PMC article.
-
Newly defined landmarks for a three-dimensionally based cephalometric analysis: a retrospective cone-beam computed tomography scan review.Angle Orthod. 2015 Jan;85(1):3-10. doi: 10.2319/021814-120.1. Angle Orthod. 2015. PMID: 24866835 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability of different three-dimensional cephalometric landmarks in cone-beam computed tomography : A systematic review.Angle Orthod. 2019 Mar;89(2):317-332. doi: 10.2319/042018-302.1. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Angle Orthod. 2019. PMID: 30423256 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of conventional versus cone-beam CT-synthesised lateral cephalograms for cephalometric analysis: A systematic review.J Orthod. 2024 Jun;51(2):160-176. doi: 10.1177/14653125231178038. Epub 2023 Jun 21. J Orthod. 2024. PMID: 37340975
Cited by
-
Development and evaluation of a convolutional neural network model for sex prediction using cephalometric radiographs and cranial photographs.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Aug 25;25(1):348. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01892-x. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40855268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mozzo P, Procacci C, Tacconi A, Martini PT, Andreis IA. A new volumetric CT machine for dental imaging based on the cone-beam technique: preliminary results. Eur Radiol. 1998;8(9):1558–64. 10.1007/s003300050586. - PubMed
-
- Palomo JM, Yang CY, Hans MG. Clinical application of Three-Dimensional craniofacial imaging in orthodontics. J Med Sci. 2005;25(6):269–78. 10.1107/S0108270184005254.
-
- Raj G, Raj M, Saigo L. Accuracy of conventional versus cone-beam CT-synthesised lateral cephalograms for cephalometric analysis: A systematic review [published online ahead of print, 2023 Jun 21]. J Orthod. 2023;14653125231178038. 10.1177/14653125231178038. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

