The impact of dietary interventions on cardiometabolic health
- PMID: 40450314
- PMCID: PMC12125738
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-025-02766-w
The impact of dietary interventions on cardiometabolic health
Abstract
Obesity and cardiometabolic diseases are leading causes of morbidity and mortality among adults worldwide. These conditions significantly contribute to and exacerbate other major causes of illness and death, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and chronic kidney disease. The growing burden of these diseases has increased the interest of modern medicine in understanding metabolic processes and health, with diet emerging as a pivotal modifiable factor, alongside physical inactivity and smoking. In this review, we discuss the pathophysiological and evolutionary foundations of metabolic processes that may link "unhealthy" nutrition to obesity and cardiometabolic diseases and review the current literature to assess the effects of various diet interventions and patterns on cardiometabolic parameters. Special emphasis is placed on summarizing the latest, albeit partially contradictory, evidence to offer balanced dietary recommendations with the ultimate aim to improve cardiometabolic health.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

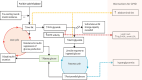
Similar articles
-
The evolution of the heart-healthy diet for vascular health: A walk through time.Vasc Med. 2020 Apr;25(2):184-193. doi: 10.1177/1358863X19901287. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Vasc Med. 2020. PMID: 32124663 Review.
-
Physical activity and metabolic syndrome severity among older adults at cardiovascular risk: 1-Year trends.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2021 Sep 22;31(10):2870-2886. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2021.06.015. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2021. PMID: 34366176
-
Identifying Patients at Risk for Cardiometabolic and Chronic Diseases by Using the Exercise Vital Sign to Screen for Physical Inactivity.Prev Chronic Dis. 2025 Jan 2;22:E02. doi: 10.5888/pcd22.240149. Prev Chronic Dis. 2025. PMID: 39745943 Free PMC article.
-
Whole grain food diet slightly reduces cardiovascular risks in obese/overweight adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020 Feb 18;20(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01337-z. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020. PMID: 32070285 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary and Policy Priorities for Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes, and Obesity: A Comprehensive Review.Circulation. 2016 Jan 12;133(2):187-225. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018585. Circulation. 2016. PMID: 26746178 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of 12 nutritional interventions on type 2 diabetes: a systematic review with network meta-analysis of randomized trials.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2025 Aug 7;22(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12986-025-00968-3. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40775771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koskinas KC, Van Craenenbroeck EM, Antoniades C, et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: an ESC clinical consensus statement. Eur Heart J. 2024;00:1–36. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae508.
-
- The top 10 causes of death. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death. Accessed 22 Sep 2024.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

