Exploring monkeypox virus antibody levels: insights from human immunological research
- PMID: 40450351
- PMCID: PMC12126862
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-025-02748-0
Exploring monkeypox virus antibody levels: insights from human immunological research
Abstract
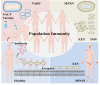
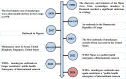
Monkeypox(mpox) is a zoonotic disease caused by the monkeypox virus (MPXV), which was previously endemic to West and Central Africa. However, it has recently appeared in several non-endemic countries beyond Africa. On July 23, 202 WHO declared mpox outbreak a public health emergency of international concern, a declaration reaffirmed on August 14, 2024. In this context, understanding the antibody levels of MPXV in the population has become crucial, especially given the historical cross-protection provided by smallpox vaccination. To provide a comprehensive overview of the current understanding of MPXV antibody levels and the protective efficacy of smallpox vaccination, we conducted a review of the existing literature. We reviewed relevant studies published in peer-reviewed journals from 1958 to 2025, focusing on those that reported research on MPXV antibodies and the effects of smallpox vaccination. Here, we review the research progress of MPXV and smallpox virus(VARV) in epidemiology, etiology, mutation and mechanism of virus infection, clinical characteristics and vaccine application. In addition, the differences in MPXV levels in different populations and the cross-protective effect of smallpox vaccine against mpox were also discussed. Our review indicates that MPXV antibody levels are closely related to the level of immunity in the population, particularly among individuals who have received smallpox vaccination. This narrative review aims to synthesize existing evidence on the role of smallpox vaccination in protecting against mpox and to offer evidence-based guidance for public health policy. We aim to establish a theoretical foundation and practical recommendations for future research and mpox prevention strategies.
Keywords: Antibody level; Monkeypox virus; Population immunity; Smallpox vaccine; Vaccine; Vaccine applicatio.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not Applicable. Consent for publication: Not Applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation between microneutralization test and a multiplexed immunoassay for evaluation of monkeypox and vaccinia virus antibodies before and after smallpox vaccination.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 23;16:1585284. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1585284. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40625755 Free PMC article.
-
Mpox Clinical Presentation, Diagnostic Approaches, and Treatment Strategies: A Review.JAMA. 2024 Nov 19;332(19):1652-1662. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.21091. JAMA. 2024. PMID: 39401235 Review.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Repurposed Smallpox Vaccines Against Mpox: A Critical Review of ACAM2000, JYNNEOS, and LC16.J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2025 Jun 24;15(1):88. doi: 10.1007/s44197-025-00432-8. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40553320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of orthopoxvirus vaccination and Mpox infection on cross-protective immunity: a multicohort observational study.Lancet Microbe. 2025 Jul;6(7):101098. doi: 10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101098. Epub 2025 Apr 28. Lancet Microbe. 2025. PMID: 40311645
-
The pathophysiological and immunological background of the monkeypox virus infection: An update.J Med Virol. 2023 Jan;95(1):e28206. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28206. Epub 2022 Oct 25. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36217803 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

